Difference Between Pineapple and Durian: Revealed!
Pineapples and durians are two tropical fruits that are vastly different in taste, texture, and aroma. Pineapples, originating from South America, are known for their sweet and tangy flavor and are popular worldwide.
Durians, native to Southeast Asia, have a creamy texture and a strong smell that some find unpleasant. While pineapples are rich in vitamin C and bromelain, durians are calorie-dense and high in fats.
The primary differences between pineapple and durian lie in their:
For example, pineapple is often used in tropical dishes and cocktails, while durian is commonly eaten raw and used in Southeast Asian sweets and savory dishes.
Understanding pineapple and durian helps to appreciate the diversity of tropical fruits and their unique contributions to global cuisine.

Key Takeaway
Pineapple vs. Durian: Comparing Tropical Fruits
| Feature | Pineapple | Durian |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | South America | Southeast Asia |
| Taste | Sweet, tangy | Sweet, complex, can be savory |
| Texture | Firm, juicy | Creamy, custard-like |
| Aroma | Fragrant, fresh | Pungent, strong |
| Nutritional Value | High in vitamin C, lower in calories | High in fats, higher in calories |
| Culinary Use | Used in cocktails, tropical dishes | Eaten raw, used in sweets and savory dishes |
| Cultural Significance | Symbol of hospitality in some cultures | Regarded as the ‘king of fruits’ in Southeast Asia |
Origins and Distribution
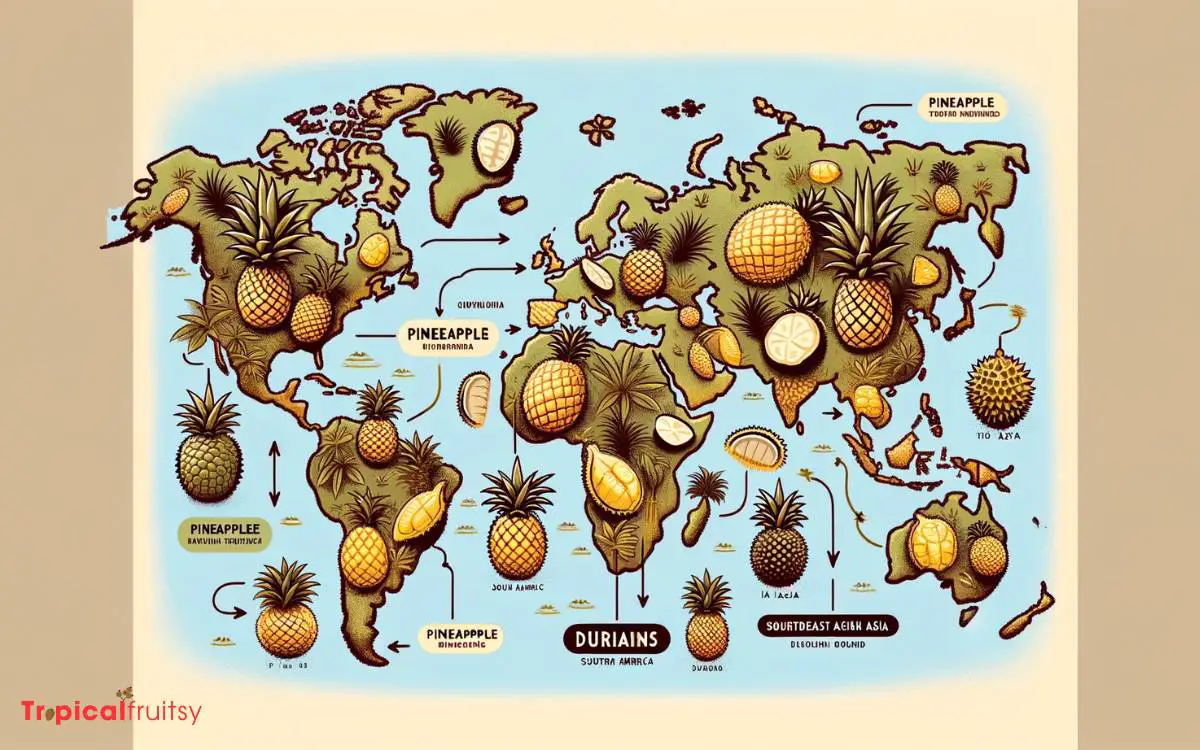
Where do the distinctive fruits pineapple and durian originate, and how has their cultivation spread globally?
Pineapples (Ananas comosus) trace their origins to South America, specifically the region between southern Brazil and Paraguay.
Through exploration and trade, they were disseminated to the Caribbean, Hawaii, the Philippines, and subsequently to other tropical regions.
Durians (Durio spp.), with their notorious aroma, are native to Southeast Asia, primarily Malaysia, Indonesia, and Borneo.
Their cultivation has remained largely within this region, although there has been a growing interest and subsequent farming expansion in other tropical areas.
The global distribution of these fruits has been influenced by factors such as colonial trade routes, climatic adaptability, and market demand, which have shaped their availability and popularity across different cultures.
Physical Characteristics
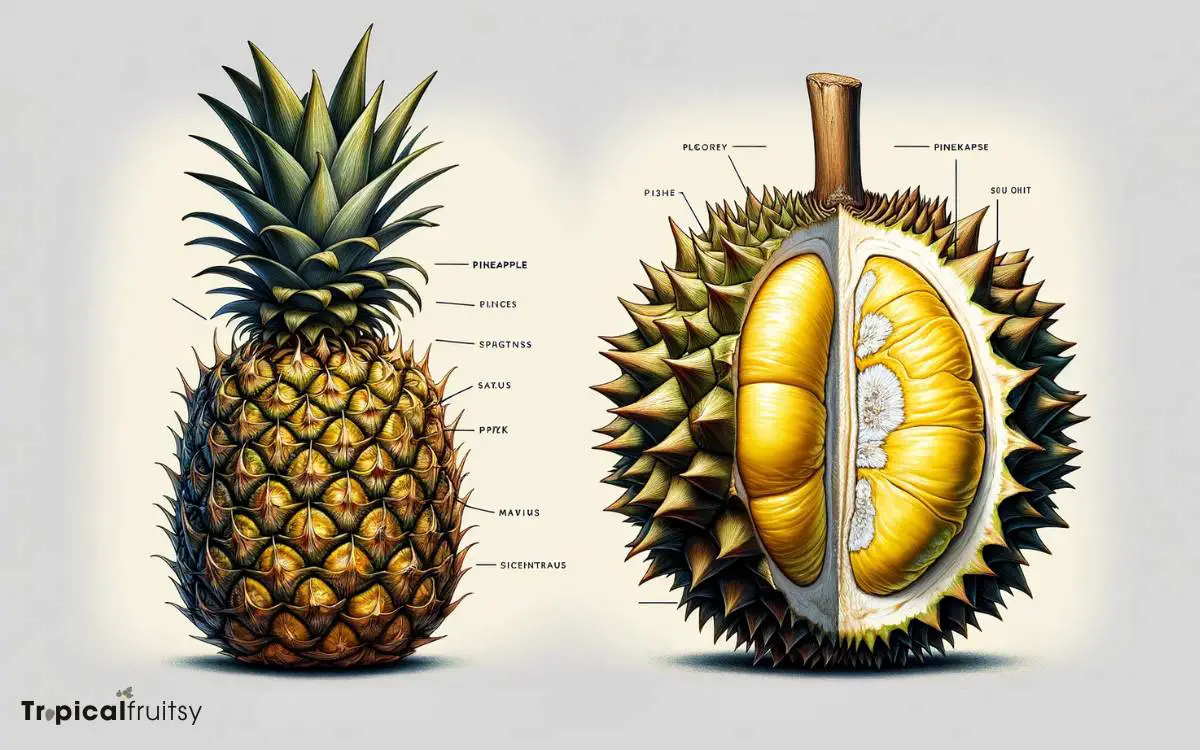
The pineapple and durian are both distinctive in their physical appearance. The pineapple is characterized by a tough, waxy exterior with spiky leaves on top.
It typically exhibits a golden-brown to greenish skin with a geometric pattern of eyes, indicative of its fibrous interior.
On the other hand, the durian is known for its large size, formidable thorn-covered husk, and strong odor. Its exterior is a formidable armor of spikes, which serves as a deterrent to natural predators.
Durians are substantially larger and heavier than pineapples, with some varieties weighing up to 7 pounds or more.
The durian’s pungent aroma is a critical identification characteristic, sharply contrasting with the pineapple’s subtle, sweet fragrance.
Aromatic Profiles

The aromatic profiles of pineapple and durian are distinctive features that contribute to their overall sensory perception.
While pineapples emit a strong sweet and tropical fragrance, durians are notorious for their pungent and divisive scent, which can be intense enough to elicit a strong reaction upon first exposure.
Analyzing the compounds responsible for these odors presents challenges due to the complexity of their volatile constituents, which can affect odor identification and characterization.
Scent Intensity Comparison
Although both pineapple and durian are tropical fruits, the intensity and profile of their scents are remarkably distinct, with durian often eliciting stronger reactions due to its pungent aroma.
When assessing the scent intensity and aromatic profiles of these fruits, the following points highlight key differences:
- Pineapple emits a sweet, tangy fragrance that is generally considered pleasant and inviting.
- Durian, by contrast, has a potent smell that is often described as a mix of sulfuric, sweet, and savory notes.
- The durian’s odor is so strong that it can permeate through packaging, leading to restrictions in certain public places.
- Sensitivity to these scents varies among individuals, with some people being attracted to durian’s aroma, while others find it repulsive.
The divergence in scent profiles significantly influences consumer preferences and the environments in which these fruits are enjoyed or avoided.
Sweet Vs Pungent
Pineapple’s aromatic profile is characterized by a refreshing sweetness, often associated with a vibrant, tropical fruitiness that is universally appealing.
This alluring bouquet primarily results from the presence of esters, compounds that provide a fruity note, and is further complemented by subtle acidic undertones which contribute to its crisp, invigorating fragrance.
In stark contrast, durian’s scent profile is notoriously pungent and complex, with a potent combination of sulfurous compounds and esters that elicit reactions ranging from deep appreciation to strong repulsion.
This olfactory duality is due to bioactive compounds that can produce odors reminiscent of various savory and sweet elements within the same fruit. Understanding these aromatic nuances presents significant odor identification challenges.
Odor Identification Challenges
Both pineapple and durian offer unique challenges in odor identification due to their complex aromatic profiles, which involve a multitude of volatile organic compounds.
The identification of specific scents within these fruits can be intricate due to:
- The presence of numerous odor-active molecules that interact in nuanced ways.
- The varying concentrations of these compounds, which can alter the perceived aroma.
- The influence of individual genetic differences in olfactory perception among humans.
- The change in aromatic profile through ripening stages, affecting scent intensity and quality.
Analytically, the odor of pineapple is typically associated with fresh, sweet, and slightly acidic notes, while durian’s scent is often described as potent, sulfurous, and complex.
Understanding these aromatic complexities is essential for both consumer acceptance and food science.
Flavor Comparisons

The flavors of pineapple and durian are markedly distinct, with the former being sweet and tangy and the latter offering a complex taste profile often described as a blend of savory, sweet, and creamy notes.
To provide a clearer comparison, consider the following table:
| Aspect | Pineapple | Durian |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Taste | Sweet and tangy | Savory, sweet, creamy |
| Texture | Juicy and fibrous | Custardy and creamy |
| Aftertaste | Refreshing with acidity | Persistent, rich flavor |
Analytically, pineapple’s acidic nature contributes to its tanginess, which complements its high sugar content, resulting in a balanced, vibrant flavor.
Durian’s flavor complexity arises from volatile sulfur compounds, which give it depth and a lingering taste that can be polarizing.
The creamy texture of durian contrasts with the fibrous bite of pineapple, enhancing the sensory experience.
Nutritional Content

When comparing the nutritional content of pineapple and durian, it is essential to examine their respective caloric values, which can influence dietary choices for individuals monitoring their energy intake.
Additionally, the variance in vitamin content between these two fruits highlights their unique contributions to a balanced diet, with each offering a distinct profile of micronutrients.
Lastly, the contrast in fiber content is a critical factor to consider, as it affects digestive health and the overall nutritional value of the fruits.
Caloric Value Comparison
Regarding nutritional content, pineapple and durian differ significantly in their caloric values, with durian being markedly higher in calories per serving.
This is not just a trivial distinction; it reflects the broader nutritional profiles of these fruits, which are shaped by their respective compositions of macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
To illustrate the caloric difference:
- A 100-gram serving of pineapple typically contains about 50 calories.
- The same serving size of durian can contain roughly 147 calories.
- Durian is richer in fats, contributing to its higher caloric density.
- Pineapple, on the other hand, is lower in fats and higher in water content, which results in fewer calories.
When considering dietary needs or weight management, this caloric disparity is a significant factor. It is essential for consumers to understand how each fruit fits into their nutritional goals.
Vitamin Content Variance
Pineapples and durians exhibit distinct vitamin profiles, with each fruit offering a unique array of essential micronutrients beneficial to health.
Pineapples are particularly rich in vitamin C, providing a robust antioxidant source that can bolster the immune system and enhance iron absorption.
They also contain moderate amounts of vitamins A and K, along with smaller quantities of B-vitamins such as folate.
Durians, on the other hand, are noteworthy for their high levels of vitamin B-complex, including niacin, riboflavin, and thiamine, which play vital roles in energy metabolism.
Additionally, durians offer a substantial amount of vitamin C, though less than pineapples, and provide vitamin A, which is crucial for maintaining healthy vision and skin.
Analyzing these vitamin content variances helps underscore the nutritional contributions these tropical fruits offer to a balanced diet.
Fiber Content Contrast
Moving beyond vitamins, the fiber content in pineapples and durians presents another significant nutritional contrast between these two fruits.
Fiber plays a critical role in digestive health, and its presence in our diet is vital for maintaining regular bowel movements and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
When comparing the two fruits:
- A cup of fresh pineapple chunks contains approximately 2.3 grams of dietary fiber.
- Conversely, one cup of durian provides about 9 grams of fiber.
This stark difference indicates that durian is a considerably richer source of fiber. The higher fiber content in durian may offer greater benefits for digestive health.
These figures illustrate the disparities in fiber contribution to the diet, positioning durian as the more potent option for fiber intake.
Culinary Uses

Both pineapple and durian are tropical fruits, each offering a unique set of culinary applications that range from raw consumption to incorporation into complex dishes.
Pineapple is renowned for its versatility; it’s used fresh, juiced, or cooked, enhancing flavor profiles in sweet and savory dishes alike.
Its acidity and tenderizing enzymes make it ideal for marinades, while its vibrant sweetness complements desserts and beverages.
Conversely, durian’s pungent aroma and custard-like texture render it a more polarizing choice. In Southeast Asia, it is revered and often consumed fresh, but it’s also integrated into pastries, ice creams, and traditional savory dishes.
Its rich, complex taste lends a distinctive depth to culinary creations that can withstand and harmonize with its assertive flavor characteristics.
Cultural Significance

Understanding the cultural significance of pineapple and durian reveals their deep-rooted roles in societal traditions and beliefs, particularly in the regions where they are indigenous.
These fruits are not merely sources of nutrition but are imbued with symbolic meanings and are integral to various cultural ceremonies and practices.
The following points highlight their significance:
- Pineapples symbolize hospitality and are often used as decorative elements in festive occasions across cultures in the Caribbean and the Americas.
- In Southeast Asia, the durian is celebrated with festivals and is considered the ‘king of fruits,’ representing abundance and social status.
- Traditional beliefs in some cultures consider the pineapple as a token of good fortune and prosperity.
- Durians, with their formidable presence, are sometimes used in spiritual rituals to ward off evil spirits.
These cultural associations underscore the fruits’ importance beyond their physical attributes.
Market Availability

The market availability of pineapples and durians varies significantly due to differences in cultivation requirements and geographic distribution.
Pineapples, being more tolerant to a range of climatic conditions, are cultivated in numerous countries across the globe.
This widespread cultivation leads to a broader market presence, making pineapples readily accessible in most regions year-round, either as fresh produce or in processed forms.
In contrast, durians require specific tropical climates for optimal growth and are predominantly grown in Southeast Asia.
Their market availability outside this region can be sporadic and is often limited to specialized Asian markets or areas with significant Southeast Asian populations.
Moreover, due to their perishable nature and distinct odor, international transportation of durians is more challenging, resulting in higher prices and reduced availability compared to pineapples.
Handling and Storage

Proper handling and storage techniques for pineapples and durians are crucial to maintain freshness and extend shelf life.
For pineapples, the primary concern is preventing overripening and spoilage, whereas with durians, managing the strong odor and delicate flesh is paramount.
To facilitate understanding, consider the following guidelines:
- Pineapples should be stored at room temperature until they ripen and then refrigerated to slow down the ripening process.
- Durians are best kept in airy, well-ventilated spaces to minimize the pungency of their aroma.
- Once cut, both fruits should be kept in airtight containers and refrigerated to preserve flavor and prevent contamination.
- Durians have a shorter shelf life and should be consumed within a few days of purchase, while pineapples can last up to a week when properly stored.
Conclusion
While the pineapple and durian share tropical origins, their divergence is pronounced in sensory and cultural dimensions.
The pineapple, with its regal crown, is the accessible monarch of tropical fruits, widely embraced for its sweet tang and versatile culinary applications.
Contrastingly, the durian, often likened to a spiky warrior, commands a niche reverence, with its pungent aroma and rich custard-like flavor.
Each fruit holds a unique place in the tapestry of global food culture, symbolizing the vastness of nature’s bounty.






