Does Durian Make You Fat? Unlocking the Truth!
Durian, a high-calorie and fat-rich fruit, can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excessive amounts.
One cup of durian provides approximately 357 calories and 13 grams of fat, which is notably higher compared to many other fruits. It is also rich in carbohydrates, primarily sugars, which can affect blood sugar levels.
However, durian contains dietary fiber and healthy fats, which can be beneficial when eaten in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Overeating durian, especially in addition to a high-calorie diet, may lead to weight gain, but moderate consumption is unlikely to have a significant impact on body weight.
Durian’s nutritional profile includes:
To enjoy durian without gaining weight:
Enjoying durian in moderation can be part of a healthy diet without derailing weight management efforts.

Key Takeaway
Nutritional Content of Durian (Per 100g Serving)
| Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
| Calories | 147 kcal |
| Total Fat | 5 g |
| Saturated Fat | 2.3 g |
| Unsaturated Fat | 2.7 g |
| Cholesterol | 0 mg |
| Sodium | 2 mg |
| Total Carbohydrates | 27 g |
| Dietary Fiber | 3.8 g |
| Sugars | 20 g |
| Protein | 1.5 g |
| Vitamin C | 19.7 mg |
| Thiamin (Vitamin B1) | 0.37 mg |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | 0.2 mg |
| Niacin (Vitamin B3) | 1.07 mg |
| Potassium | 436 mg |
| Magnesium | 30 mg |
| Iron | 0.43 mg |
Understanding Durian’s Nutritional Profile

Durian’s nutritional profile is characterized by its high caloric density, primarily due to its significant carbohydrate content. This tropical fruit is also a source of dietary fats, which contribute to its overall energy value.
Despite the high energy content, durian contains beneficial nutrients such as vitamin C, potassium, and dietary fiber.
The presence of these nutrients suggests potential health benefits, including antioxidant properties and support for cardiovascular health.
However, when considering the impact on weight, the caloric content is a critical factor. The consumption of durian, like any calorically dense food, should be moderated based on individual dietary needs and physical activity levels.
Understanding the exact calorie count in a typical serving will further illuminate the potential implications for weight management.
Calorie Count in a Typical Serving
When assessing the impact of durian on weight management, it is crucial to consider the caloric content of a typical serving.
A standard serving of durian, which is approximately 100 grams, contains about 147 calories, indicating a relatively high energy density for a fruit.
Comparatively, this calorie content is important to analyze in the context of daily dietary intake and energy expenditure.
Serving Size Calories
A typical serving of durian, weighing approximately 100 grams, contains about 147 calories. To provide a clearer picture, the calorie content of durian can be compared to other common fruits based on a similar serving size.
The following table presents a concise comparison:
| Fruit | Serving Size (grams) | Calories |
|---|---|---|
| Durian | 100 | 147 |
| Banana | 100 | 89 |
| Apple | 100 | 52 |
| Mango | 100 | 60 |
This indicates that while durian is nutrient-dense, it is also calorie-dense, which could contribute to weight gain if consumed in large quantities without considering overall daily caloric intake.
Energy Density Comparison
How does the energy density of durian compare to that of other popular fruits in terms of calorie content per serving?
To objectively analyze, we consider the calories per typical serving size. Durian, known for its rich taste and creamy texture, also packs a substantial caloric punch. A typical serving of durian (about one cup, or 243 grams) can contain around 357 calories.
In contrast, the same serving size of apple provides approximately 52 calories, while a banana offers closer to 105 calories. Even avocado, another calorie-dense fruit, provides fewer calories at about 234 per cup.
Thus, durian’s energy density is indeed higher than many common fruits, which suggests that moderation is key if one is monitoring caloric intake for weight management purposes.
Durian’s Fat Content Explained
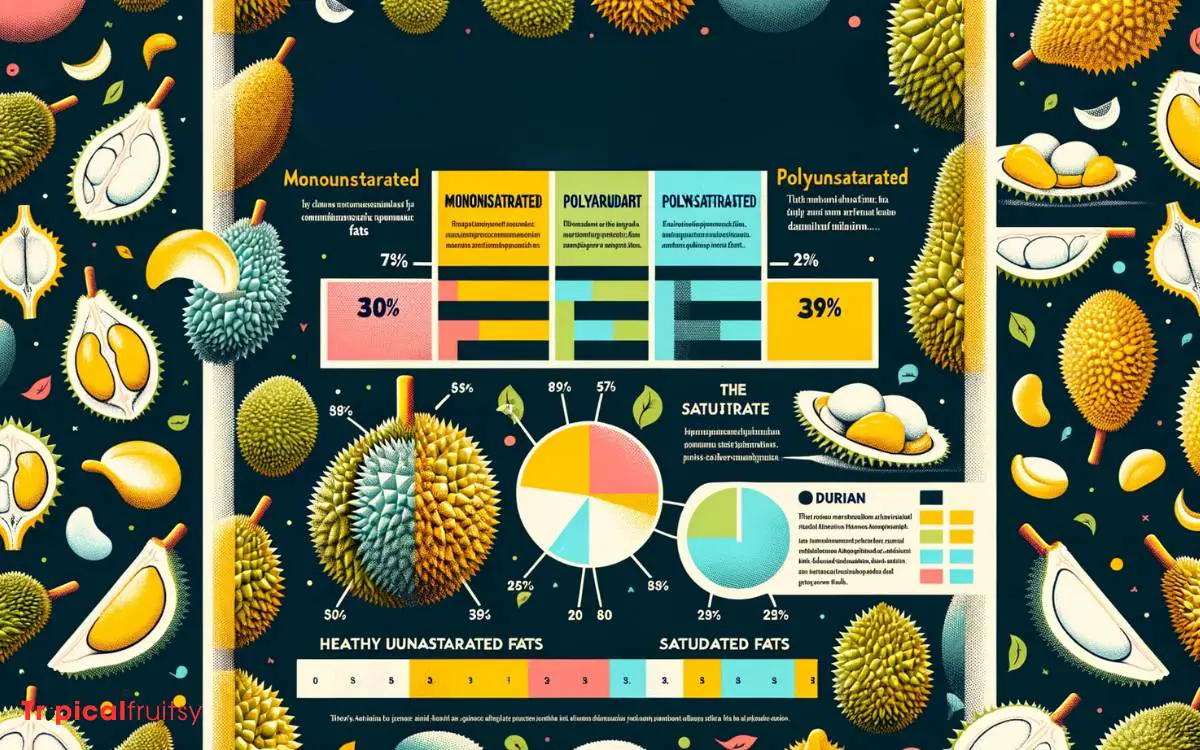
Regarding its macronutrient composition, durian contains a significant amount of fat compared to other fruits, which contributes to its higher calorie content.
This fat is primarily composed of unsaturated fats, which are considered healthier than saturated fats found in many animal products.
However, the presence of fat in durian does necessitate moderation in consumption, especially for individuals monitoring their caloric intake.
Consider the following:
- A single durian fruit can contain up to 13 grams of fat.
- This fat contributes to roughly 23% of the total caloric value of the fruit.
- Durian’s high fat content is a key factor in its rich, creamy texture that many find irresistible.
Understanding the fat content in durian is crucial for assessing its role in a balanced diet.
Impact on Blood Sugar Levels

Why should those concerned with blood sugar fluctuations consider the glycemic index of durian in their dietary choices?
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a food can raise blood glucose levels. Foods with a high GI can lead to rapid spikes, potentially problematic for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
Durian, with its naturally occurring sugars, can impact blood sugar levels. However, the effect may vary based on ripeness and individual metabolic responses.
| Nutrient | Amount per Serving | Impact on Blood Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Total Carbohydrates | Approx. 27g (100g serving) | Moderate |
| Dietary Fiber | Approx. 3.8g | Slows Glucose Absorption |
| Glycemic Index | 49 (moderate) | Gradual increase |
Understanding the nuances of durian’s GI is essential for informed dietary decisions.
Comparing Durian to Other Fruits

When assessing the potential weight gain effects of durian, it is essential to compare its caloric content, nutrient density, and sugar levels to those of other commonly consumed fruits.
Studies have shown that calorie for calorie, fruits can differ significantly in their macronutrient composition and fiber content, which are factors relevant to weight management.
An analytical review of durian in the context of these variables will provide a clearer understanding of its place in a balanced diet compared to other fruit options.
Caloric Content Comparison
In comparison to other popular fruits, durian contains significantly more calories, contributing to its reputation as a potentially weight-gain-promoting food.
For those who are mindful of their caloric intake, understanding how durian stacks up against other fruits can be insightful.
Here are some comparisons:
- A 100-gram serving of durian has about 147 calories.
- The same serving size of apples has approximately 52 calories.
- Bananas provide closer competition at around 89 calories per 100 grams.
The caloric density of durian is evident when juxtaposed with these common fruits. It is dense, both in nutrients and energy, warranting moderation for those managing their weight.
Consuming durian in large quantities could lead to a higher caloric intake than anticipated, potentially affecting one’s diet and weight objectives.
Nutrient Density Variance
Although durian is higher in calories than many other fruits, it also offers a unique nutrient profile that includes vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
When examining its nutrient density, durian is particularly rich in vitamin C, B-vitamins such as thiamin and niacin, as well as minerals like potassium and magnesium.
These elements are crucial for maintaining various bodily functions, from immune responses to energy metabolism.
In contrast, fruits such as apples or berries may be lower in caloric content but also provide a different constellation of nutrients, often with higher fiber content and less fat.
Durian’s fat content, primarily composed of healthy monounsaturated fats, contributes to its caloric density, yet it is essential for nutrient absorption.
This nuanced comparison underscores the importance of considering overall dietary patterns rather than single food items.
Shifting focus to sugar content, it is imperative to understand how durian’s carbohydrate composition influences its potential impact on weight.
Sugar Levels Contrast
Regarding sugar content, durian contains higher levels of simple carbohydrates compared to many other fruits, which may influence its potential to contribute to weight gain if consumed in large quantities.
To provide a clearer picture:
- Mango: A cup of mango has about 23 grams of sugar, while the same amount of durian can contain up to 30 grams.
- Banana: One medium banana holds approximately 14 grams of sugar, whereas a single serving of durian may offer nearly double that amount.
- Apple: With about 19 grams of sugar in a medium-sized apple, durian still surpasses it, showcasing its comparatively high sugar composition.
These figures underscore the importance of moderation, especially for individuals monitoring their sugar intake.
Consuming durian within the context of a balanced diet is critical to avoid any negative impacts on weight and overall health.
Durian in a Balanced Diet

Within the context of a balanced diet, durian can be enjoyed in moderation without necessarily leading to weight gain.
The key to incorporating durian, or any food with substantial calorie content, lies in understanding portion control and the overall caloric balance of one’s diet.
Durian, while rich in sugars and fats, also provides dietary fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, contributing to nutritional diversity when consumed as part of a varied diet.
Analytical consideration of durian’s energy density compared to its nutrient value suggests that it should be consumed judiciously, especially considering individual metabolic rates and physical activity levels.
Mindful consumption of durian, aligning with dietary guidelines that emphasize fruits and vegetables, can prevent excessive caloric intake.
This nuanced approach underscores that dietary choices are just one aspect influencing body weight, leading to the consideration of lifestyle factors and weight gain.
Lifestyle Factors and Weight Gain

Physical activity, dietary habits, sleep patterns, and stress levels are pivotal lifestyle factors that influence weight gain, independent of specific foods like durian.
While moderate consumption of durian can fit into a balanced diet, overlooking these key factors may lead to an energy imbalance and subsequent weight gain.
Consider the following aspects:
- Sedentary Behavior: Lack of physical exercise can reduce metabolic rate, leading to the accumulation of excess calories as fat.
- Sleep Deprivation: Inadequate sleep has been linked to increased hunger and appetite, potentially causing overeating.
- Chronic Stress: High stress levels can stimulate the appetite and drive cravings for energy-dense foods.
These elements, supported by empirical evidence, demonstrate that weight management is multifaceted. An analytical approach to lifestyle choices is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight.
Conclusion
Durian, with its high caloric density and significant fat content, can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess.
However, when integrated judiciously into a balanced diet, its nutritional benefits can be enjoyed without necessarily leading to obesity.
An interesting statistic reveals that a single durian can contain up to 1,350 calories, underscoring the importance of portion control.
Ultimately, lifestyle factors play a pivotal role in determining the impact of durian on an individual’s weight.






