How to Grow Durian Fruit? 7 Easy Steps!
Growing durian fruit successfully involves understanding its unique requirements and providing optimal growing conditions. Durians thrive in warm tropical climates and require fertile, well-drained soil.
The process starts with the selection of a high-quality cultivar suitable for the local climate and market. Planting should be done with care, providing the trees with space to grow and a stable foundation.
Regular watering, proper fertilization, and pruning are essential for the health of the durian trees. Effective pest and disease management ensures the trees remain healthy.
Harvesting durians at the right time and handling them with care during storage are crucial to maintaining the fruit’s quality.
Durian cultivation is a delicate process that requires:
Mastering durian cultivation can yield bountiful harvests of this unique and highly valued tropical fruit.

Key Takeaway
Understanding Durian Varieties
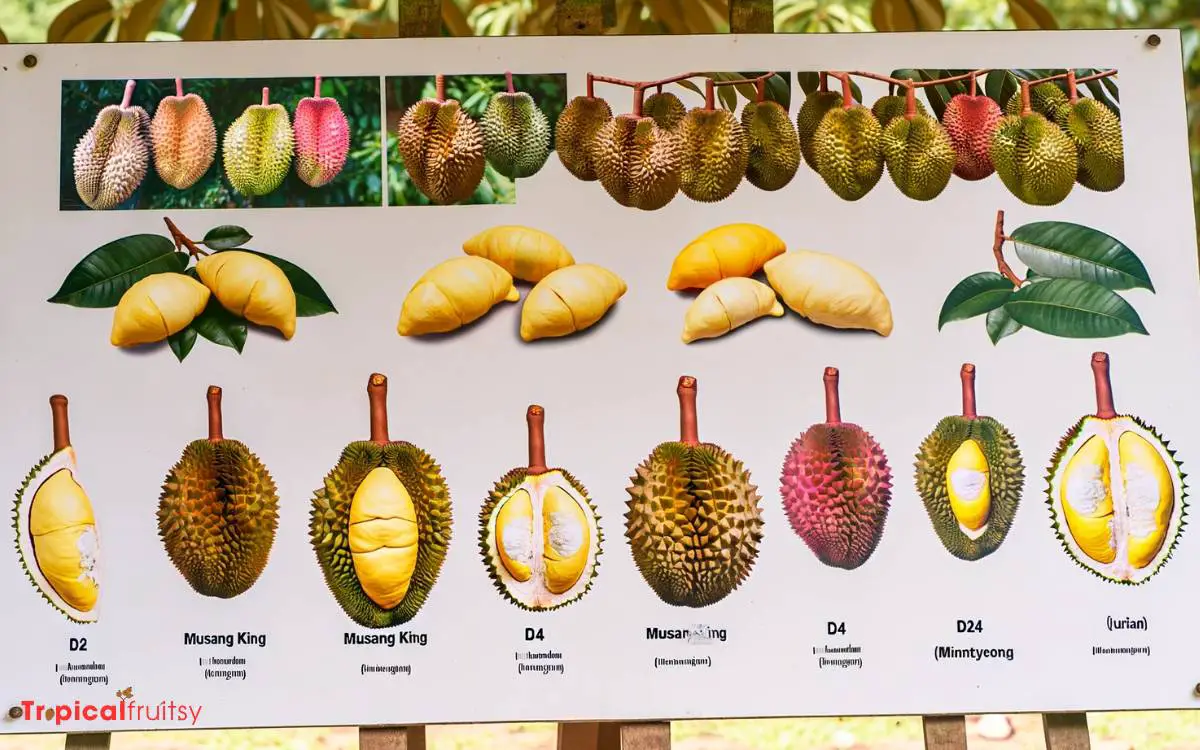

Selecting from the numerous durian varieties is a crucial step in the cultivation process, as each possesses unique characteristics and growth requirements.
Durians, scientifically known as Durio spp., display a wide genetic diversity, with more than 30 species identified within Southeast Asia.
The cultivars range from the popular Musang King, lauded for its creamy texture and sweet taste, to the more pungent and bitter D24 Sultan.
These varieties differ not only in flavor profiles but also in tree size, resistance to pathogens, and climatic adaptability.
Understanding the phenological phases, from flowering to fruit development of different durian varieties, is imperative for successful cultivation. A meticulous approach to variety selection can substantially influence yield and fruit quality.
With the appropriate variety chosen, attention must then turn to the intricacies of choosing a planting location.
Step 1: Choosing a Planting Location
Site selection is paramount in durian cultivation, requiring well-draining soil, ample sunlight, and protection from strong winds for optimal tree growth and fruit production.
Durian trees thrive in a climate marked by warm temperatures and high humidity, with conditions mimicking their native tropical habitat. The elevation should not exceed 800 meters, as higher altitudes can adversely affect growth.
| Factor | Ideal Condition | Reason for Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Drainage | Well-draining | Prevents root rot and supports aeration |
| Sunlight | Full sun (6+ hours daily) | Maximizes photosynthesis |
| Wind Protection | Sheltered location | Reduces physical damage to the tree |
| Elevation | Below 800 meters | Ensures suitable temperature range |
| Humidity | High | Mimics native tropical environment |
Selecting a location with these parameters ensures a robust foundation for durian tree establishment.
As the site is finalized, attention must then shift to preparing the soil, enabling the durian trees to establish with vigor.
Step 2: Preparing the Soil

How, then, should one prepare the soil to provide the optimal conditions for durian tree growth?
Soil preparation is a crucial step in cultivating durian trees, which demand specific conditions to thrive.
Here are the paramount considerations:
- pH Level: Ensure a slightly acidic to neutral pH, ideally between 6 and 7.
- Soil Composition: Aim for rich, organic loam with good drainage to prevent waterlogging.
- Nutrient Content: Incorporate well-rotted manure or compost to enrich the soil with essential nutrients.
- Soil Depth: Durian roots require deep soil, at least 1-2 meters of unimpeded depth.
- Aeration: Till the soil to improve oxygenation, promoting healthy root development.
With the soil meticulously prepared, the stage is set for the next critical phase: planting your durian tree.
Step 3: Planting Your Durian Tree

Moving on from soil preparation, the next step is to plant your durian sapling at the appropriate time, which is typically at the beginning of the rainy season.
This timing ensures that the sapling has access to adequate moisture, which is essential for the establishment of a strong root system.
When planting, dig a hole twice as wide and just as deep as the root ball of your sapling. Carefully place the sapling in the center, ensuring that the top of the root ball is level with the surrounding soil surface.
Backfill the hole with a mix of native soil and compost, gently tamping down to eliminate air pockets.
Water thoroughly after planting and mulch around the base to conserve moisture and regulate soil temperature. Regular watering, especially during dry spells, is critical for young durian trees.
Step 4: Watering and Fertilization

A durian tree’s growth and fruit production heavily rely on consistent watering and a well-planned fertilization schedule.
Optimal hydration and nutrient provision are crucial for the tree’s health and the development of its distinctive fruit.
To achieve this, consider the following:
- Watering: Durian trees require deep watering, especially during dry periods. Ensure the soil is moist but not waterlogged.
- Young Trees: Newly planted trees need frequent watering until established.
- Fertilization: Apply a balanced NPK (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) fertilizer during the growing season.
- Organic Matter: Incorporate compost or well-rotted manure to improve soil fertility.
- Micronutrients: Durian trees occasionally need additional micronutrients, such as zinc or boron, to prevent deficiencies.
Regular monitoring and adjustments based on soil tests will optimize conditions for durian trees to thrive.
Step 5: Pruning and Maintenance

Pruning is a crucial horticultural practice for durian trees. It is essential for shaping the tree, removing unproductive or diseased branches, and promoting optimal fruit production.
Precise pruning techniques, tailored to the durian tree’s growth habits and developmental stages, can enhance air circulation and light penetration. These factors are vital for tree health and fruit quality.
Establishing a regular maintenance schedule that includes systematic inspection and timely pruning interventions is fundamental for sustaining a productive durian orchard.
Optimal Pruning Techniques
Effective pruning is essential for maintaining the health and productivity of durian trees. This involves the careful removal of certain branches to improve air circulation and sunlight penetration.
When pruning durian trees, it is important to apply the following techniques:
- Selective Thinning: Remove only the necessary branches to minimize stress on the tree.
- Heading Cuts: Shorten branches to encourage new growth and fruit production.
- Cleaning Cuts: Eliminate dead or diseased wood to prevent the spread of pathogens.
- Structural Pruning: Shape the tree for optimal strength, especially when young, to support the weight of mature fruit.
- Timing: Conduct pruning during the dormant season to reduce sap loss and enhance healing.
Understanding and implementing these techniques will contribute to a successful cultivation.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Having established the importance of optimal pruning techniques, it is now critical to adhere to a regular maintenance schedule to ensure the ongoing vitality and productivity of durian trees.
Pruning should be conducted annually, during the trees’ dormant period, to remove dead or diseased wood and to shape the canopy for optimal light penetration and air circulation, which are essential for fruit set and quality.
Additionally, regular application of well-balanced fertilizers, suited to the specific soil conditions and tree age, is imperative to maintain nutrient levels conducive to durian tree health and fruit production.
As we focus on these fundamental horticultural practices, we must also remain vigilant against potential threats.
Step 6: Pest and Disease Management

To ensure healthy durian crops, growers must vigilantly control a myriad of pests and diseases that can severely impact fruit production.
Successful management hinges on an integrated approach that combines cultural practices with the judicious use of chemical and biological controls.
Specific strategies include:
- Regular Monitoring: Systematic scouting for signs of infestation or disease to enable early intervention.
- Sanitation: Removing fallen fruits and pruning to reduce habitats for pests and disease vectors.
- Fungicide and Insecticide Application: Targeted use of chemicals based on identified threats and life cycle stages of pests.
- Biological Controls: Introduction of natural predators or parasitoids to manage pest populations.
- Quarantine Measures: Isolating affected trees to prevent spread of diseases like Phytophthora palmivora, which causes durian fruit rot.
Adherence to these measures will mitigate the risk of outbreaks and safeguard yields.
Step 7: Harvesting and Storage

As you approach the culmination of your durian growing efforts, precise timing and proper techniques are crucial for harvesting and storing these unique fruits.
Durians typically reach maturation approximately 3 to 4 months after flowering. Indications of ripeness include a subtle change in the hull color and a distinctive, pungent aroma.
It’s imperative to harvest durians after they naturally fall to the ground to ensure peak ripeness and flavor, rather than picking them directly from the tree.
For storage, durians are highly perishable and must be handled with care. Keep the fruits at ambient temperatures if they are to be consumed within a few days, or refrigerate to prolong freshness for up to 5 days.
For extended storage, freezing the pulp can maintain the fruit’s integrity for several months.
Conclusion
Successful cultivation of durian fruit demands meticulous attention to detail. This includes selecting the appropriate variety and preparing the soil. It also involves consistent care in watering, fertilizing, and pruning.
Furthermore, vigilance in pest and disease management is imperative to ensure the health of the tree.
As the adage goes, ‘Patience is a virtue,’ which holds true for durian cultivation. The reward of harvesting this unique and aromatic fruit is a testament to the grower’s dedication and expertise.






