Is Breadfruit Good for Keto? A Nutritional Analysis!
No, breadfruit is not considered a good option for the ketogenic diet as it is high in carbohydrates which could disrupt ketosis.
The ketogenic diet is a low-carb, high-fat diet that involves significantly reducing carbohydrate intake and replacing it with fat to put the body into a metabolic state known as ketosis.
Breadfruit, despite its nutritional benefits, is high in carbohydrates. A single cup of breadfruit can contain around 60 grams of carbs, which is more than the entire daily allowance on a keto diet, which typically limits net carb intake to 20-50 grams per day.
Since the goal of keto is to maintain ketosis for fat burning, consuming high-carb foods like breadfruit can hinder this process.
For example, if someone on a keto diet eats a portion of breadfruit, they might ingest too many carbs, which can:
Opt for keto-friendly alternatives such as cauliflower or zucchini to maintain ketosis instead of high-carb breadfruit.

Key Takeaway
8 Aspect: Breadfruit and Keto Diet
| Aspect | Breadfruit and Keto Diet |
|---|---|
| Carbohydrate Content | Relatively High |
| Dietary Fiber | Moderately High |
| Sugar Content | Natural Sugars Present |
| Net Carbohydrates (per 100g) | Approximately 22.22g |
| Ketogenic-Friendly | Generally Not Suitable |
| Portion Control | Limited Use in Small Portions |
| Alternative Low-Carb Options | Consider Low-Carb Vegetables, Nuts, and Seeds |
| Consultation with Dietitian | Advised for Customized Guidance |
Understanding the Keto Diet

The ketogenic diet hinges on the principle of drastically reducing carbohydrate intake to prompt the body into a state of ketosis.
This nutritional approach focuses on high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carb foods to shift the body’s metabolism away from burning glucose and towards burning fat for energy.
Scientific studies have demonstrated that following a ketogenic diet can lead to weight loss, improved blood sugar control, and other health benefits.
By keeping carbohydrate levels low, typically below 50 grams per day, the body depletes its glucose reserves and initiates ketosis, a metabolic state in which ketone bodies become the primary source of fuel.
As we explore the compatibility of different foods with this diet, it’s important to consider their macronutrient composition
What Is Breadfruit

Originating from the South Pacific, breadfruit is a starchy tropical fruit that is related to jackfruit and figs. Revered for its versatility, breadfruit has a texture similar to bread when cooked, which accounts for its name.
The fruit is green and globular, with a bumpy surface, and can grow to the size of a large melon. Its flesh is rich in complex carbohydrates and fiber, providing a substantial energy source.
Nutritionally, breadfruit also contains moderate amounts of essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, potassium, and various antioxidants that are integral to maintaining health.
In regions where it is grown, breadfruit is not just a dietary staple but also an important cultural element, often featured in traditional dishes and culinary practices.
Breadfruit Nutritional Breakdown

Regarding the nutritional composition of breadfruit, it is predominantly composed of carbohydrates, with a single cup serving (around 220 grams) providing approximately 60 grams of carbs, which includes fiber, making it a high-carb food unsuitable for a ketogenic diet.
The table below summarizes the key nutritional components of breadfruit:
| Nutrient | Amount per cup (~220g) |
|---|---|
| Calories | 227 |
| Carbohydrates | 60g |
| Dietary Fiber | 11g |
| Protein | 2.4g |
The high carbohydrate content, including dietary fiber, is an important consideration for anyone following a ketogenic diet, which requires low carb intake to maintain ketosis.
The modest amount of protein and caloric content also contribute to the overall nutritional profile but do not mitigate the high carb factor for ketogenic purposes.
Carbs in Breadfruit: Analysis

In analyzing the carbohydrate content of breadfruit, it is evident that its high level of carbs poses a challenge for inclusion in a ketogenic diet.
The ketogenic diet strictly limits carbohydrates to induce a state of ketosis, where the body burns fat for energy rather than glucose.
To create a vivid picture regarding the carb content in breadfruit, consider the following:
- A typical serving of breadfruit (about 220 grams) contains approximately 60 grams of carbohydrates.
- This serving size delivers about 10 grams of dietary fiber, which reduces the net carbs to 50 grams.
- In the context of a keto diet, the daily carb limit is often set below 50 grams.
- Therefore, a single serving of breadfruit could potentially exhaust an individual’s entire carbohydrate allowance for the day.
The Ketosis Process Explained
Understanding the ketosis process is crucial for appreciating why high-carbohydrate foods like breadfruit are typically excluded from a ketogenic diet.
Ketosis is a metabolic state in which the body, deprived of glucose from carbohydrates, shifts to burning fatty acids and ketone bodies for energy.
This process is the cornerstone of the ketogenic diet, which restricts carbohydrate intake to typically 20-50 grams per day, prompting the body to utilize fat as its primary fuel source.
Achieving ketosis requires strict adherence to this macronutrient allocation, as excessive carbohydrate consumption can halt ketone production.
Consequently, foods like breadfruit, with a higher carb content, can disrupt this delicate balance, pulling the individual out of ketosis and negating the metabolic benefits sought through such a dietary regimen.
Pros and Cons of Breadfruit
We must weigh the nutritional benefits of breadfruit against its high carbohydrate content to determine its suitability for a ketogenic diet.
The pros and cons of breadfruit can be summarized as follows:
- High in Fiber: Breadfruit is a good source of dietary fiber, which can aid in digestion and help maintain a healthy gut.
- Rich in Nutrients: It contains essential vitamins and minerals such as vitamin C, potassium, and antioxidants.
- Carbohydrate Density: Breadfruit has a high carbohydrate content, which can quickly exceed the daily carb limit of a ketogenic diet.
- Glycemic Impact: Its glycemic index is relatively high, which could disrupt ketosis and impede the metabolic state essential for a successful keto diet.
How Does Breadfruit’s Carbohydrate Content Affect Its Suitability for a Keto Diet?
Breadfruit’s carbohydrate content is relatively high, making it unsuitable for a keto diet. With around 27 grams of carbs per 100-gram serving, breadfruit may hinder ketosis. To stay within keto limits, it’s best to opt for low-carb alternatives like cauliflower or zucchini.
Keto-Friendly Alternatives to Breadfruit
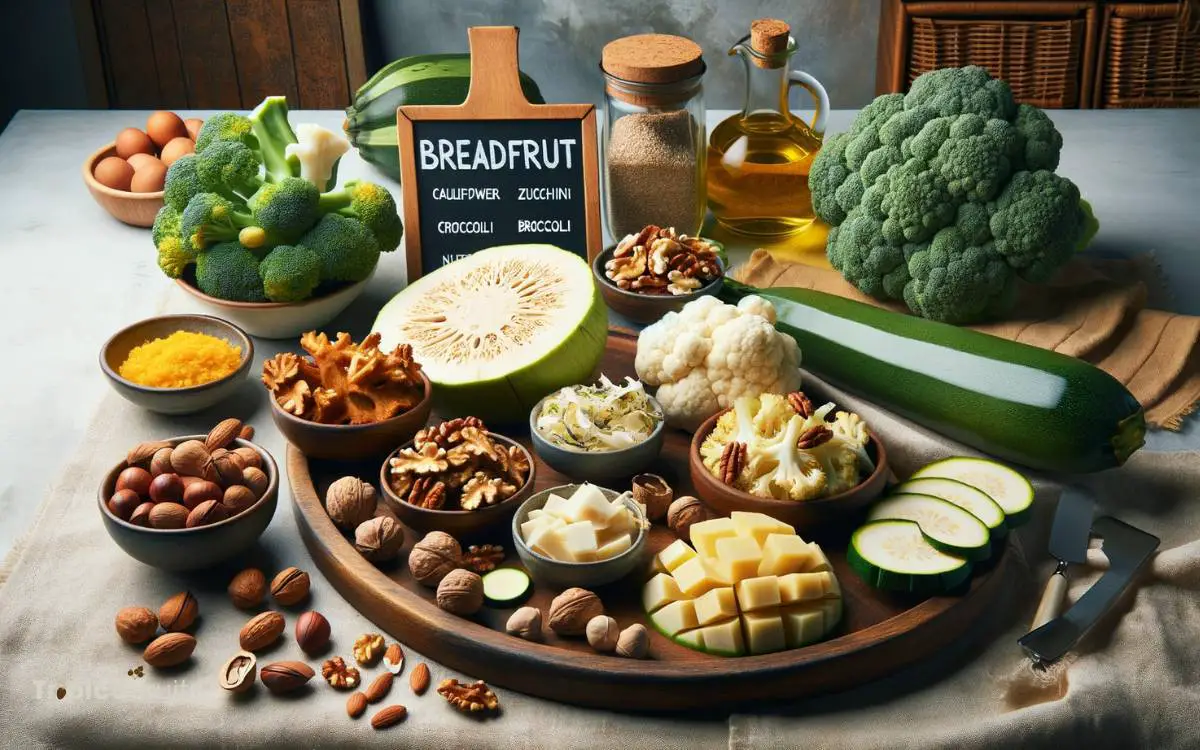

Given the high carbohydrate content of breadfruit, individuals following a ketogenic diet may consider several low-carb alternatives to maintain their state of ketosis.
These alternatives should ideally be rich in dietary fiber and low in net carbs to align with the ketogenic principles.
The following table provides a comparison of suitable substitutes:
| Alternative | Net Carbs (per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Cauliflower | 3g |
| Zucchini | 2g |
| Spaghetti Squash | 5.5g |
| Eggplant | 3g |
| Portobello Mushrooms | 2g |
These alternatives not only offer a lower carbohydrate count but also embody versatility in culinary applications, allowing for a seamless integration into a keto-friendly diet.
It is critical to consider the total daily carbohydrate intake when incorporating these foods into meal planning.
Conclusion
Breadfruit, with its higher carbohydrate content, diverges from the foundational principles of the ketogenic diet, which restricts such macronutrients to maintain ketosis.
While offering nutritional benefits, its carbohydrate density precludes it from being a keto-friendly option.
Alternatives with lower carbohydrate profiles are recommended for adherence to the ketogenic regimen, highlighting the necessity of selecting foods that align with the dietary framework’s macronutrient ratios for effective ketogenic maintenance.






