Is Durian a Fruit or Vegetable? Unlocking the Mystery!
Durian is a fruit, specifically a tropical fruit known for its large size, unique odor, and spiky husk. It is native to Southeast Asia and highly valued for its custard-like flesh.
The durian is classified as a fruit because it grows from the flowers of the Durio species of trees and contains seeds.
It is recognized by certain characteristic features:
Durian is consumed fresh and is also used in various culinary preparations, including desserts and savory dishes.
Despite its polarizing scent, durian is often referred to as the “King of Fruits” in Southeast Asia, reflecting its esteemed status among fruit lovers in the region.

Key Takeaway
What Is Durian?
Durian is a tropical fruit known for its large size, distinctive spiky exterior, and strong odor. Botanically classified as Durio, it is a member of the Malvaceae family, a group that also includes other species such as hibiscus and okra.
The fruit’s flesh, which can range in color from pale yellow to red, is encased within a hard husk that requires careful handling due to its sharp thorns.
The aroma of durian is quite potent, often described as a mixture of savory, sweet, and sulfurous notes, and it is this characteristic that elicits strong reactions ranging from fondness to intense aversion.
Nutritionally, durian is rich in carbohydrates, fats, and dietary fiber, making it a substantial energy source in diets within its native regions.
Botanical Classification Explained

Classifying durian botanically, it falls unequivocally into the category of fruit due to its role as the mature ovary of a flowering plant, containing seeds that facilitate plant reproduction.
In botanical terms, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure that develops from the ovary after flowering.
Durians belong to the genus Durio and are part of the Malvaceae family, which places them among other well-known fruits such as hibiscus and cotton.
The durian’s distinctive characteristics include its large size, unique odor, and spiky outer shell. These features are adaptations that have evolved to encourage dispersal of seeds by animals who consume the fleshy part of the fruit.
From a methodical standpoint, categorizing durian as a fruit is consistent with the criteria established by plant morphology and reproductive biology.
Characteristics of Fruits
While vegetables are typically defined by their culinary uses, fruits, including the durian, are distinguished by their role in plant reproduction, bearing seeds that are encased within a sweet or savory edible tissue.
Analyzing the characteristics of fruits reveals a methodical framework for classification:
- Development from the flower: Fruits originate from the fertilized ovary of a flower and contain seeds, which are the propagative component of the plant.
- Variety of structures: Fruits exhibit a wide range of morphologies, from simple fleshy structures like berries and drupes to more complex forms such as aggregate and multiple fruits.
- Nutritional content: They typically provide a rich source of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and sugars, which are essential for the human diet and attract animals for seed dispersal.
Durian’s Unique Features
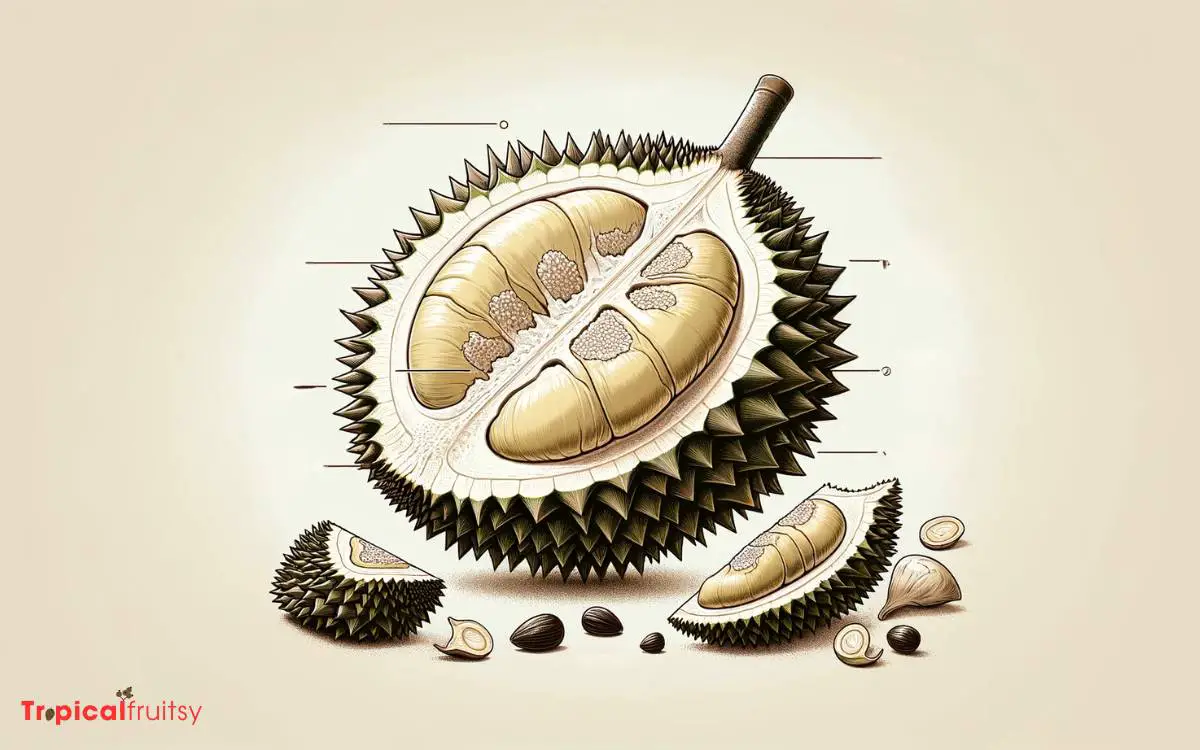

The durian, known for its distinctive odor and formidable thorn-covered husk, is a tropical fruit with unique characteristics that set it apart from other members of the fruit kingdom.
In order to convey the singular attributes of the durian effectively, an analytical examination is presented herein.
| Feature | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Odor | Pungent smell that is often compared to rotten onions or turpentine |
| Husk | Thick, spiky outer layer that requires careful handling |
| Taste | Rich custard-like flavor with hints of almond |
| Nutritional Value | High in carbohydrates, fats, and dietary fiber |
| Cultural Significance | Revered in Southeast Asia as the “King of Fruits” |
Resolving the Durian Debate

Although some may question the categorization of durian due to its unconventional characteristics, it is unequivocally classified as a fruit based on botanical criteria.
The scientific demarcation between fruits and vegetables is clear-cut, with fruits being the mature ovary of a flowering plant, typically containing seeds.
Durian fits this description as it develops from the flower of its respective tree and houses seeds within its fleshy body.
To further engage and inform the audience, here are some additional points:
- Botanical Definition: A fruit is the mature ovary of a plant, usually containing seeds; durian meets this specification.
- Development Process: Durian develops from the pollinated flower of the Durio tree, following the typical lifecycle of fruit-bearing flora.
- Anatomical Structure: Encasing its seeds, the durian’s edible flesh is characteristic of fruit rather than vegetable matter.
Conclusion
The durian is botanically classified as a fruit, specifically a multiple fruit, due to its characteristics such as containing seeds, deriving from a flower, and having a fleshy or pulpy exterior when mature.
Despite its polarizing reputation, akin to the enigmatic Sphinx of yore, the durian’s identity is unequivocally established within the scientific community, effectively resolving any debate regarding its status in the plant kingdom.






