Is Durian High in Sugar? Unveiling its Sugar Content Impact!
Durian, known as the ‘king of fruits,’ is relatively high in sugar, containing about 27 grams of sugar per cup of pulp.
Durian is a tropical fruit distinguished by its large size, unique odor, and formidable thorn-covered husk. It’s a sweet, custard-like fruit that’s popular in Southeast Asia.
Despite its nutritional benefits, durian has a high sugar content, which can be a concern for those monitoring their sugar intake.
For individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels, consuming durian in moderation is essential.
The high sugar content in durian is naturally occurring, as with most fruits, and it also comes with dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals, providing a nutritive balance.
While durian’s high sugar content might deter some, its unique taste and nutritional profile make it a worthwhile treat when enjoyed in moderation.

Key Takeaway
The Durian Basics

One must understand that durian, often referred to as the ‘king of fruits,’ is a tropical species native to Southeast Asia, renowned not only for its distinctive odor but also for its rich, custardy texture.
This fruit’s large size, unique flavor, and nutritional profile make it a subject of interest for many. Durians contain a variety of essential nutrients, including dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Despite its creamy texture, it is important to note that durian is relatively high in natural sugars and calories, which can contribute to its overall sweet taste.
Its sugar content can be a concern for individuals monitoring their carbohydrate intake, making it essential to consider portion sizes when consuming this potent fruit.
Understanding Sugar Content

When assessing the sugar content of durian, it is crucial to distinguish between natural sugars, inherent in the fruit, and any added sugars that may be present in processed durian products.
The natural sugar levels in durian are relatively high compared to other fruits, which is an important consideration for individuals monitoring their sugar intake.
Understanding the impact of these sugar levels on health is imperative, especially for those with dietary restrictions or conditions such as diabetes.
Natural Vs. Added Sugars
Understanding the distinction between natural sugars, as found in fruits like durian, and added sugars is crucial in evaluating their nutritional impact.
Natural sugars are inherent in foods, while added sugars are incorporated during processing or preparation.
Considering durian, it’s important to recognize that:
- It contains natural sugars primarily in the form of fructose and glucose.
- These sugars come with fiber, vitamins, and minerals also present in the fruit.
- Added sugars, in contrast, provide ‘empty calories’ with no nutritional benefits.
- The body metabolizes natural and added sugars differently, affecting health outcomes.
Eating fruits like durian offers more than just sweetness; you also get a variety of nutrients. Conversely, added sugars can contribute to health issues like obesity and diabetes when consumed in excess.
Durian Sugar Levels
Despite its nutritional benefits, durian is relatively high in natural sugars, with an average serving containing approximately 27 grams of carbohydrates, most of which are sugars.
This level of sugar content places durian on the higher end of the spectrum when compared to other fruits.
For context, an apple of a similar weight contains about 19 grams of carbohydrates. It’s important for consumers, particularly those monitoring their sugar intake, to be aware of this fact.
The sugars in durian are primarily composed of sucrose, fructose, and glucose, which can impact blood sugar levels.
For individuals with diabetes or those following a low-sugar diet, portion control and careful monitoring of durian consumption are advisable to maintain balanced nutritional practices.
Health Implications
The sugar content in durian has significant implications for individuals with metabolic conditions such as diabetes and obesity.
A high intake of sugary foods can exacerbate these conditions, leading to further health complications. It is crucial for such individuals to monitor their consumption of fruits like durian.
- Glycemic Index: Durian has a moderate glycemic index, which means it can cause a relatively gradual increase in blood sugar levels.
- Portion Control: Due to its sugar content, portion size should be carefully managed.
- Nutrient Density: Despite its sugar content, durian is rich in nutrients, providing potential health benefits when consumed in moderation.
- Individual Response: Blood sugar response to durian can vary between individuals, necessitating personalized dietary adjustments.
Those concerned about their sugar intake should consult with healthcare professionals to understand the role of durian in their diet.
Durian Vs. Other Fruits
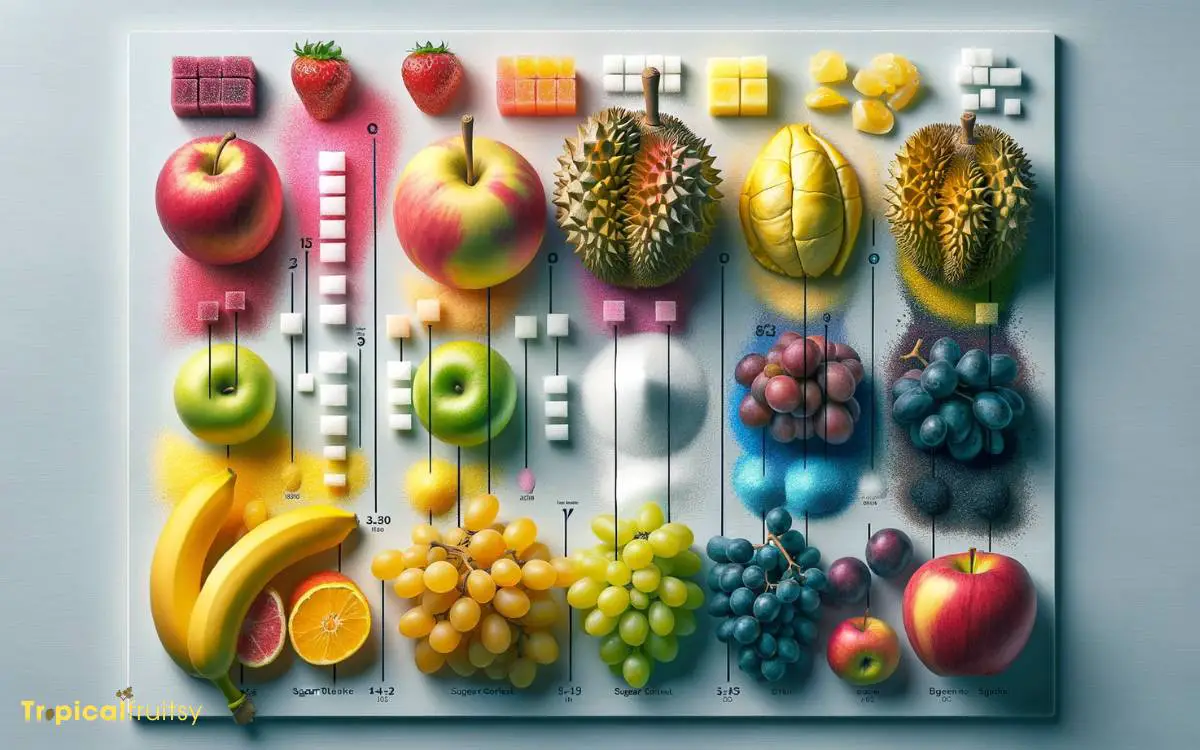
When comparing the sugar content of durian to other fruits, it is evident that this Southeast Asian delicacy typically contains more sugar per serving.
A single cup of durian can have upwards of 30 grams of sugar, which is considerably higher than many common fruits.
For example, an apple of a similar weight has approximately 19 grams of sugar, while a cup of sliced strawberries contains about 7 grams. Bananas, known for their higher sugar content, have about 18 grams per medium-sized fruit.
The high sugar content in durian contributes to its intensely sweet flavor profile, which is a distinguishing characteristic of the fruit. It’s important for consumers to be aware of this when considering durian as part of a balanced diet.
Nutritional Breakdown
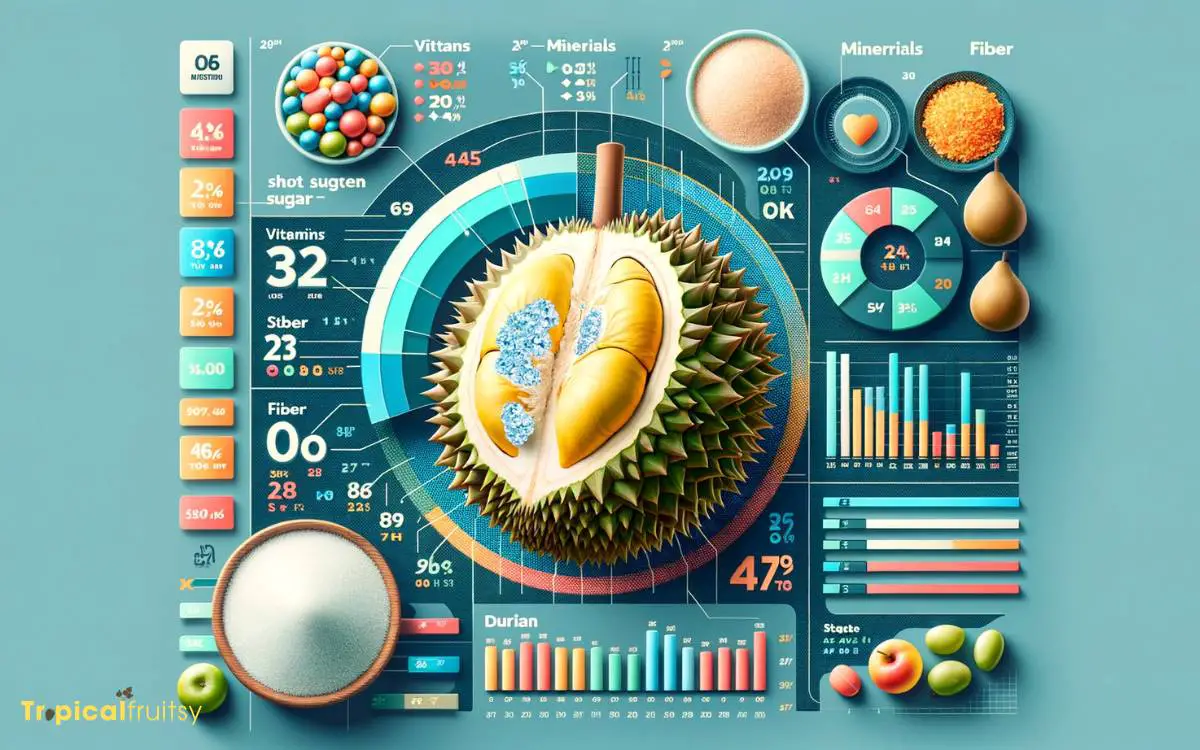
Beyond its sugar content, durian offers a rich array of nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber.
This tropical fruit is often hailed for its nutritional benefits, which makes it a worthwhile inclusion in a balanced diet despite its sweetness.
Here are some of the key nutritional components found in durian:
- Vitamins: Durian is particularly high in vitamin C, which is essential for immune function, and it also provides good amounts of thiamin and vitamin B6.
- Minerals: It contains minerals such as potassium, which is important for heart health, and magnesium.
- Dietary Fiber: A notable amount of dietary fiber aids in digestion and can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
- Antioxidants: Durian has antioxidants that may protect cells from oxidative stress.
Thus, durian’s nutritional profile is complex and extends beyond simple sugar content.
Health Benefits Explored

How does the consumption of durian, despite its sugar content, contribute to overall health and well-being?
Durian is rich in vitamins and minerals, offering a substantial amount of vitamin C, which is pivotal for immune function, skin health, and wound healing.
The presence of B vitamins, particularly thiamine and niacin, is essential for energy metabolism and overall cell health.
Durian also contains dietary fiber, which benefits digestive health and may help in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome. Minerals like potassium support cardiovascular health by regulating blood pressure.
Moreover, durian has antioxidants that combat oxidative stress and inflammation, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases. While mindful of its sugar content, consuming durian can be part of a balanced diet.
Risks of High Sugar Intake

Acknowledging the nutritional benefits of durian, it is equally important to consider the risks associated with its high sugar content, as excessive intake can lead to serious health issues such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
Consuming high amounts of sugar can disrupt the balance of energy intake and expenditure, leading to weight gain.
Moreover, high sugar diets are linked to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as they can cause spikes in blood glucose levels and insulin resistance.
Noteworthy risks of high sugar consumption include:
- Elevated blood pressure and inflammation, contributing to heart disease.
- Increased likelihood of developing dental problems like cavities.
- A higher potential for fatty liver disease due to excess fructose intake.
- Risk of developing insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.
Choosing foods with natural sugars and monitoring overall sugar intake are essential for maintaining good health.
Durian Varieties Compared

When comparing durian varieties, it is essential to consider that sugar content may vary significantly between types. These variations are often accompanied by distinct taste profiles, which can range from intensely sweet to subtly bitter.
Accurate assessment of these differences is crucial for understanding the nutritional implications of consuming different durian cultivars.
Sugar Content Variation
Different durian varieties exhibit varying levels of sugar content, making it essential to compare them to understand their nutritional differences fully.
The sugar content in durian can fluctuate based on several factors including species, ripeness, and cultivation conditions.
Here are notable examples of how sugar content can differ among varieties:
- Musang King: Known for its creamy texture and sweet taste, often has higher sugar levels.
- D24: This variety is less sweet, suggesting a moderate sugar content.
- Red Prawn: Characterized by its orange flesh, it can be quite sweet, indicating higher sugar levels.
- Green Bamboo: Tends to have a milder sweetness, which may reflect lower sugar content.
Understanding these variations is crucial for consumers with dietary restrictions or sugar intake concerns.
Taste Profile Differences
The sugar content in various durian varieties significantly influences their respective taste profiles, with some exhibiting a distinctly sweeter flavor while others offer a more subdued sweetness.
For instance, the Musang King variety is renowned for its rich and creamy texture accompanied by a potent sweet taste, often with a hint of bitterness that adds complexity.
On the other hand, the D24 variety presents a slightly less intense sweetness, balanced with a creamier, more custard-like consistency.
The Red Prawn variety, aptly named for its reddish flesh, delivers a more nuanced sweetness with a touch of alcoholic fermentation aftertaste.
These taste nuances are crucial for consumers and growers alike, as they dictate preference, market value, and suitability for various culinary applications.
Balancing Durian in Your Diet

One must consider the high sugar content of durian when incorporating it into a balanced diet. As with any energy-dense food, moderation is key to maintaining nutritional equilibrium.
To balance durian consumption within a healthy dietary pattern, individuals should be mindful of the following:
- Portion Size: Limit servings to a small portion to keep sugar intake in check.
- Meal Timing: Consume durian as part of a meal rather than as a standalone snack to help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Nutritional Pairing: Pair durian with foods high in fiber, protein, or healthy fats to slow digestion and absorption of sugars.
- Overall Diet: Ensure that durian intake is balanced with a variety of other fruits and vegetables that provide a range of nutrients without excessive sugar.
Making Informed Choices

In light of durian’s sugar content, making informed choices about consumption is crucial for those monitoring their dietary sugar intake.
Durian, a fruit known for its unique smell and taste, also contains a significant amount of sugar.
As such, individuals with diabetes or those trying to maintain a low-sugar diet should consider the sugar content in durian along with their overall carbohydrate intake.
Portion size is key; consuming durian in moderation can allow for enjoyment of the fruit without excessive sugar consumption.
Additionally, pairing durian with foods high in fiber, protein, or healthy fats can help slow the absorption of sugar and mitigate spikes in blood glucose levels.
Being mindful of these factors enables individuals to enjoy durian while managing their dietary needs responsibly.
Conclusion
While the prodigious durian may boast a symphony of nutrients, its sugar content is not to be ignored.
As consumers navigate the treacherous waters of fruit indulgence, the durian stands as a testament to the age-old adage, ‘too much of a good thing.’
In moderation, the durian can be a beneficial addition to one’s diet; however, overconsumption could unwittingly lead to a sweet surrender to the siren call of sugar.






