Is Jackfruit the Same as Durian? Unveiling the Distinctions!
Jackfruit and durian are two distinct tropical fruits, each with unique characteristics. Jackfruit is known for its large size, sweet flavor, and meaty texture, often used as a meat substitute in vegetarian dishes.
Durian, on the other hand, is infamous for its strong odor, creamy texture, and complex taste that some describe as a blend of savory, sweet, and creamy flavors.
While both fruits have spiky exteriors and are native to Southeast Asia, they are not the same and are used differently in culinary practices.
Despite their similar appearances, jackfruit and durian are different in several key aspects:
Explore the exotic tastes and textures of jackfruit and durian, two unique fruits that enliven culinary traditions with their distinct flavors.
Key Takeaway
Jackfruit vs Durian: A Comprehensive Comparison
| Feature | Jackfruit | Durian |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Southeast Asia | Southeast Asia |
| Size | Large, up to 35 kg | Large, up to 3 kg |
| Exterior | Green or yellow, spiky | Green, spiky |
| Taste | Sweet, subtle | Intense, sweet-savory-creamy |
| Texture | Firm, fibrous | Soft, creamy |
| Smell | Sweet, fruity | Strong, pungent |
| Nutritional Value | Lower in calories, high in fiber | Higher in fat, contains unique amino acids |
| Culinary Uses | Meat substitute, desserts | Fresh consumption, sweet dishes |
Identifying Jackfruit and Durian
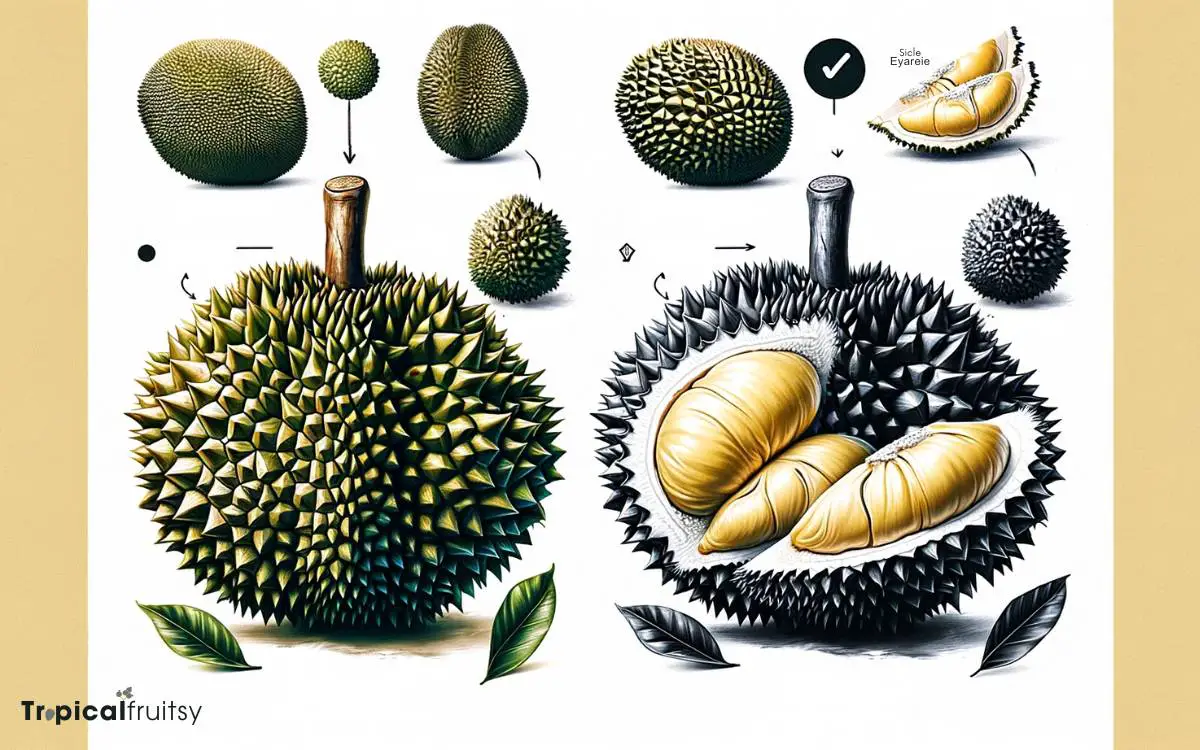

Regarding identification, jackfruit and durian can be distinguished by their distinct size, shape, and exterior texture.
The jackfruit is typically larger, reaching up to 35 kilograms in weight, with an oblong to pear-like shape and a green to yellowish exterior that is covered in blunt spikes.
Conversely, durian fruits are generally smaller, with a more rounded shape, and can weigh up to 3 kilograms. Their husk is covered in sharp, hard spines that are more pronounced than those of the jackfruit.
Additionally, while the surface of a jackfruit is relatively hard, the durian’s outer shell is tough and requires careful handling.
These morphological characteristics are crucial for the correct identification and differentiation of these two exotic fruits.
Flavor Profiles Explored

In terms of flavor, jackfruit and durian offer vastly different culinary experiences. Jackfruit is sweet and fruity, often compared to a combination of apple, pineapple, mango, and banana.
Its taste is universally pleasing, with a subtle sweetness and flavor complexity that lends itself well to both sweet and savory dishes.
On the other hand, durian is known for its potent, custard-like taste that is an acquired preference for many. It has a strong, pungent smell that can be off-putting to some people.
Durian possesses a divisive taste profile; some describe it as rich and creamy, with notes of almond. However, others are put off by what they perceive as overripe or rotten undertones.
The distinctive olfactory signature of durian can overpower its creamy sweetness, making it a fruit that polarizes opinion.
Textural Differences Highlighted
Beyond flavor, the textural qualities of jackfruit and durian diverge significantly. Jackfruit boasts a meaty, fibrous consistency, while durian has a creamy, custard-like texture.
To paint a clearer picture:
- Jackfruit: Its texture can be compared to that of pulled pork or chicken, making it a popular meat substitute in vegetarian cuisine. The flesh is dense and can be easily shredded, lending itself well to savory dishes.
- Durian: Often described as buttery, the flesh can squish between your fingers, and its smoothness is akin to rich pudding. This texture makes durian unique and can be quite polarizing for those unaccustomed to it.
- Handling: Jackfruit’s firmness allows for more versatile culinary applications, while durian’s softness requires more delicate handling.
Exploring these textural nuances leads us to consider their nutritional profiles. How does the fibrous jackfruit compare to the creamy durian in terms of health benefits?
Nutritional Values Compared
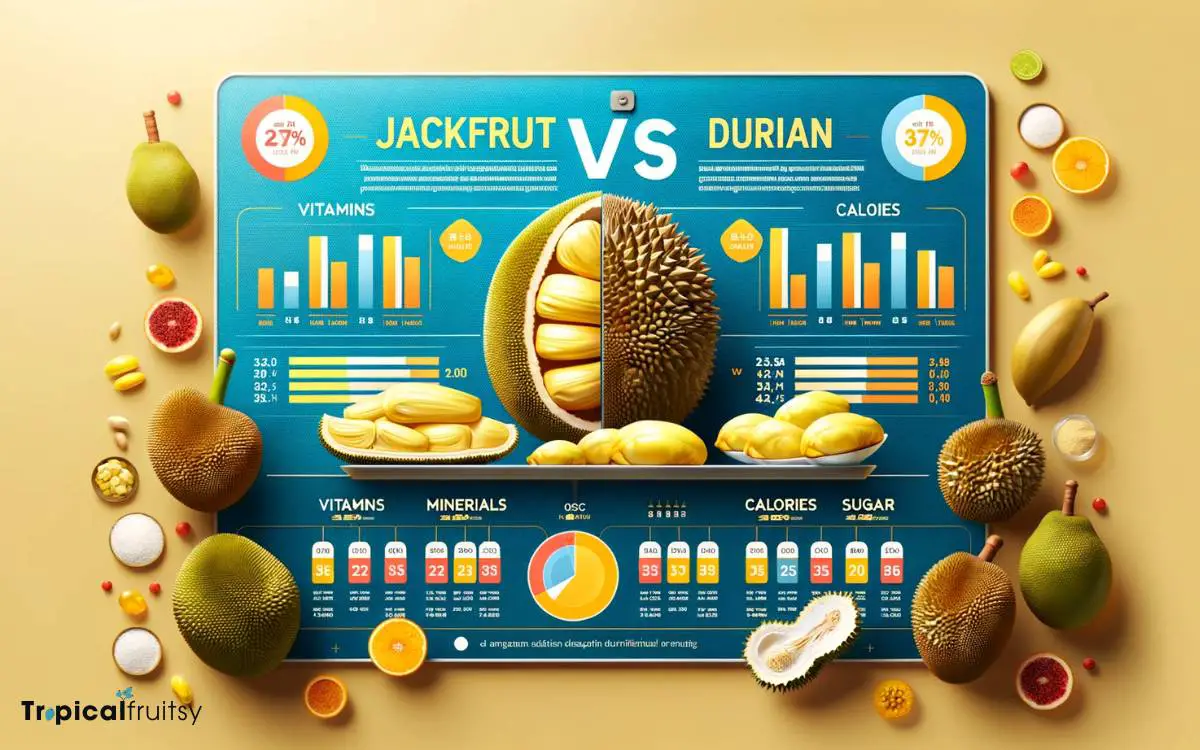

One may find substantial differences in the nutritional content of jackfruit and durian, reflecting their distinct roles in a balanced diet.
Jackfruit is rich in dietary fiber, which aids in digestion, and provides a lower calorie content than durian. It is also packed with vitamin C and B vitamins, essential for energy metabolism and immune function.
In contrast, durian boasts a higher caloric density, due to its significant fat content, which is uncommon for fruits.
Durian is also rich in thiamine and potassium, nutrients that are critical for nerve function and cardiovascular health respectively. However, both fruits offer a range of antioxidants that combat oxidative stress.
Cultural and Culinary Uses
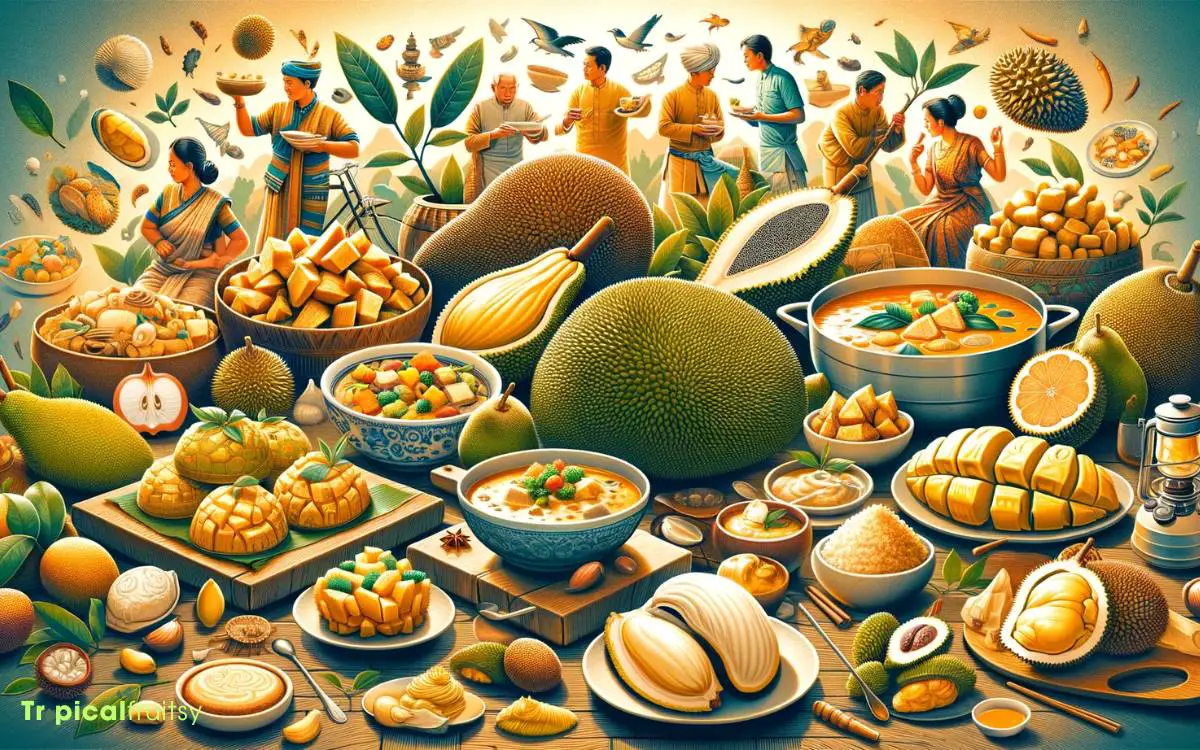

Jackfruit and durian each play distinctive roles in the culinary traditions and cultural practices of various Southeast Asian countries.
These tropical fruits are not only valued for their unique flavors and textures but also for their significance in social and religious events.
- Jackfruit: Often used as a meat substitute in vegetarian dishes, jackfruit is a versatile ingredient that can be eaten ripe or unripe. It is commonly incorporated into curries, stews, and even desserts in countries like India, Bangladesh, and Thailand.
- Durian: Revered as the ‘King of Fruits’, durian is predominantly consumed fresh and is a beloved delicacy in Malaysia, Singapore, and Indonesia. Despite its pungent odor, it is celebrated in festivals and savored in a myriad of confections.
- Cultural Significance: Both fruits are integral to local gastronomy and festivities, with durian often being the centerpiece at feasts and jackfruit symbolizing prosperity and abundance in certain cultural rituals.
Conclusion
In the compendium of tropical fruits, the colossal jackfruit and the formidable durian stand as titans, each boasting a unique amalgamation of characteristics that decisively set them apart.
Despite superficial similarities, they diverge substantially in taste, texture, and nutritional composition, further accentuated by their distinct cultural and culinary roles.
This exploration illuminates the profound dissimilarities veiled beneath their spiky exteriors, ensuring that these fruit giants are recognized not as botanical twins, but as individual marvels of nature’s bounty.