What Is an Acai Berry? The Ultimate Superberry Primer!
The acai berry is a nutrient-dense superfruit from the acai palm tree found in the Amazon rainforest.
It is celebrated for its antioxidant properties and numerous health benefits. Acai berries are small, round, and dark purple, resembling grapes but with less pulp.
They have been an integral part of Amazonian diets for generations and are renowned for their health-promoting qualities.
Here are some key points about acai berries:
Acai berries can be enjoyed in various forms, including in smoothies, acai bowls, and juices, and are compared to other berries for their superior nutritional value.
Acai berries are not only a powerhouse of nutrition but also a versatile addition to a wholesome diet.

Key Takeaway
Nutrient Benefits Overview
| Nutrient | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Antioxidants | Reduces oxidative stress |
| Dietary Fiber | Supports digestive health |
| Heart-Healthy Fats | Promotes cardiovascular health |
| Vitamins A, C, E | Essential for overall health |
| Minerals | Includes potassium and calcium |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Essential fats for brain and heart health |
Origins and History

Originating from the rainforests of Central and South America, the acai berry has been a staple in the diet of indigenous peoples for thousands of years.
This small, dark purple fruit is harvested from the acai palm tree, known scientifically as Euterpe oleracea.
Historically, it provided a significant source of nourishment and was revered for its healing properties.
Ethnobotanical studies indicate that the acai berry was also utilized in traditional medicine, with applications ranging from treating digestive disorders to skin conditions.
The harvesting methods employed by the indigenous populations ensured sustainability, enabling the acai palm to remain a renewable resource.
As modern science explores its potential health benefits, acai’s rich history continues to be a testament to its enduring nutritional value.
Nutritional Breakdown

The acai berry is densely packed with essential nutrients, including a significant number of antioxidants, amino acids, and fatty acids.
These berries contain a unique profile of dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals that contribute to their overall nutritional value.
The table below provides a concise overview of the key nutritional components found in a 100-gram serving of acai berries:
| Nutrient | Quantity |
|---|---|
| Calories | 70 |
| Total Fat | 5 grams |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5 grams |
| Carbohydrates | 4 grams |
| Dietary Fiber | 2 grams |
| Sugars | 2 grams |
| Protein | 1 gram |
| Vitamin A | 15 IU |
| Calcium | 20 milligrams |
This nutritional makeup supports the body’s essential functions and contributes to the maintenance of good health.
Health Benefits Explored
The acai berry’s health benefits are primarily attributed to its high antioxidant content, which may neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress.
Studies have suggested that the consumption of acai may support heart health by improving cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of heart disease.
Additionally, there is growing interest in the potential of acai berries as an adjunct to weight loss regimens due to their fiber content and possible metabolic effects.
Antioxidant Powerhouse
Why are acai berries considered an antioxidant powerhouse? These small, deep purple fruits are bursting with compounds known as anthocyanins, which give them their rich color and exceptional antioxidant properties.
Antioxidants are crucial in combatting oxidative stress in the body, a process linked to chronic diseases and aging.
Acai berries’ dense nutritional profile offers a myriad of health benefits, substantiated by scientific research.
| Emotion | Antioxidant Benefit | Impact on Well-being |
|---|---|---|
| Rejuvenation | Combats oxidative stress | Promotes cellular health |
| Vitality | Supports heart health | Enhances overall vitality |
| Empowerment | Boosts immune function | Strengthens body defense |
| Serenity | Reduces inflammation | Encourages calm and balance |
| Inspiration | Protects against aging | Inspires a youthful spirit |
Heart Health Improvement
Many studies suggest that the high anthocyanin content in acai berries contributes significantly to cardiovascular health.
These deep-purple fruits contain potent compounds that have been shown to have a positive impact on blood lipid profiles.
Specifically, the anthocyanins in acai berries can help to lower LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, which is often referred to as ‘bad’ cholesterol because it can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
In addition to reducing bad cholesterol levels, acai berries also promote better blood circulation. The anti-inflammatory properties of acai may support the overall function of the endothelium—the inner lining of blood vessels—enhancing vascular health. This can potentially reduce the risk of heart-related issues.
Weight Loss Aid
Acai berries are often marketed as a weight loss aid due to their potential effects on metabolism and appetite suppression.
These small, dark purple fruits have been at the center of health and diet discussions, with proponents highlighting several ways in which they may support weight loss efforts:
- Metabolic Boost: Acai berries contain amino acids and essential fatty acids, which some studies suggest can aid in boosting metabolism, potentially leading to increased fat burn.
- Appetite Suppression: The fiber found in acai berries can help promote feelings of fullness, reducing overall calorie intake.
- Energy Increase: Nutrients in acai may help improve energy levels, possibly enhancing physical activity and exercise performance.
- Antioxidant Properties: Acai is rich in antioxidants that may aid in reducing oxidative stress, which is associated with obesity and related metabolic disorders.
Common Uses and Recipes

The acai berry is commonly blended into smoothies, used as a topping for granola bowls, and featured in various health-conscious recipes due to its nutritional benefits and distinct flavor.
The deep purple fruit is often pureed to create a thick base for the popular Brazilian acai bowl, which is garnished with an assortment of fruits, nuts, and seeds.
Due to its high antioxidant content, acai is also incorporated into juices and energy bars, providing a nutritious boost.
In the culinary world, acai berries are sometimes used to make sauces that accompany meats, bringing a touch of sweetness and a vibrant color to dishes.
As a versatile ingredient, the acai berry enhances both the nutritional value and aesthetic appeal of recipes it is added to.
Comparing Acai to Other Berries
Nutritional superiority is often attributed to the acai berry when contrasted with other commonly consumed berries, such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries.
Here are some comparative insights:
- Antioxidant Content: Acai berries have a higher concentration of antioxidants compared to blueberries and strawberries, contributing to better cell protection against oxidative stress.
- Fatty Acids: Unlike most berries, acai contains omega-9 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are beneficial for cardiovascular health.
- Fiber: Acai provides more dietary fiber per serving than raspberries, aiding in digestive health and satiety.
- Calcium: The acai berry has a higher calcium content than blueberries, important for bone health.
These comparisons underline the unique nutritional profile of acai, although all berries offer valuable health benefits.
Sustainability and Harvesting

The sustainability of acai berry production hinges on responsible harvesting practices that ensure the long-term viability of palm species native to the Amazon basin.
These practices have a significant environmental impact, as they help maintain biodiversity and prevent deforestation in a region critical to global ecological balance.
Moreover, the harvesting of acai berries supports local economies by providing income for indigenous communities and small-scale farmers who rely on this activity as a primary source of revenue.
Harvesting Practices
We must consider the harvesting practices of acai berries, as they play a crucial role in the sustainability of the ecosystems where these berries grow.
Responsible harvesting methods help maintain the balance of the rainforest and support the local communities that depend on acai cultivation for their livelihood.
To ensure sustainability, several practices are commonly followed:
- Selective Harvesting: Only ripe acai berries are handpicked, allowing the plant to continue growing and producing fruit.
- Eco-friendly Transportation: Berries are often transported by riverboats to minimize carbon emissions.
- Supporting Local Harvesters: Prioritizing local workers helps sustain the regional economy and traditional practices.
- Certification Programs: Implementation of certifications like Fair Trade or Organic ensures ethical and environmentally sound harvesting methods.
These practices underscore the importance of integrating environmental stewardship with economic viability.
Environmental Impact
Sustainability plays a pivotal role in the cultivation of acai berries, influencing both the ecological balance of the Amazon and the economic stability of its harvesters.
As a non-timber forest product, acai palm harvesting, when done sustainably, can provide a viable economic alternative to deforestation for logging and agriculture, which are significant threats to the region.
Harvesting techniques that avoid damaging the acai palms and their surrounding environment ensure the regeneration and long-term health of the Amazon’s ecosystems.
Moreover, the acai berry industry’s demand has led to conservation efforts and the promotion of organic and fair-trade certifications.
These initiatives aim to minimize harmful agricultural practices, maintain biodiversity, and support the livelihoods of local communities, thereby fostering an environmentally responsible stewardship of this precious resource.
Local Economies Support
While acai berry production has the potential to bolster local economies, it is essential that sustainable harvesting methods are employed to ensure the economic benefits are long-lasting and ethically grounded.
The harvesting and sale of acai berries can provide significant financial support for local communities, particularly in the Amazon region where these berries are native.
However, to maintain this positive impact, several key practices should be prioritized:
- Implementing eco-friendly harvesting techniques that prevent deforestation and preserve biodiversity.
- Encouraging fair trade practices to ensure farmers receive a fair price for their labor.
- Providing education and resources to enable local farmers to adopt sustainable agriculture methods.
- Establishing community-based management of acai production to keep the economic benefits within local communities.
These steps will help to create a sustainable economic model around acai berry production.
Acai in Traditional Medicine
Although not widely recognized in modern pharmacology, the acai berry has been a staple in traditional Amazonian medicine for centuries.
Indigenous tribes have long utilized the berry for its purported healing properties, often consuming it to build immunity, combat fevers, and treat various ailments.
The acai berry is particularly revered for its high concentration of antioxidants, which are believed to help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body.
Traditional medicine practices also suggest that acai may aid in digestive health and can be used as a detoxifying agent.
While these traditional uses are supported by anecdotal evidence, scientific research is ongoing to substantiate the medicinal benefits of acai berries.
As such, they remain an intriguing component of ethnobotany and a subject of interest for integrative health approaches.
Purchasing and Storage Tips

Commonly found in health food stores and supermarkets, acai berries should be purchased with care and stored properly to maintain their nutritional value.
When selecting acai products, consider the following:
- Freshness: Opt for frozen or dried acai berries if fresh ones are not available, as these forms retain most of the fruit’s nutrients.
- Origin: Check the label for the country of origin and choose products sourced from the Amazon region to ensure authenticity.
- Preservation Method: Look for acai that has been freeze-dried or flash-pasteurized, as these methods best preserve the berry’s antioxidant properties.
- Storage: Store acai berries or products in a cool, dark place and consume them before the expiration date to maximize health benefits.
What Do Acai Berries Look Like
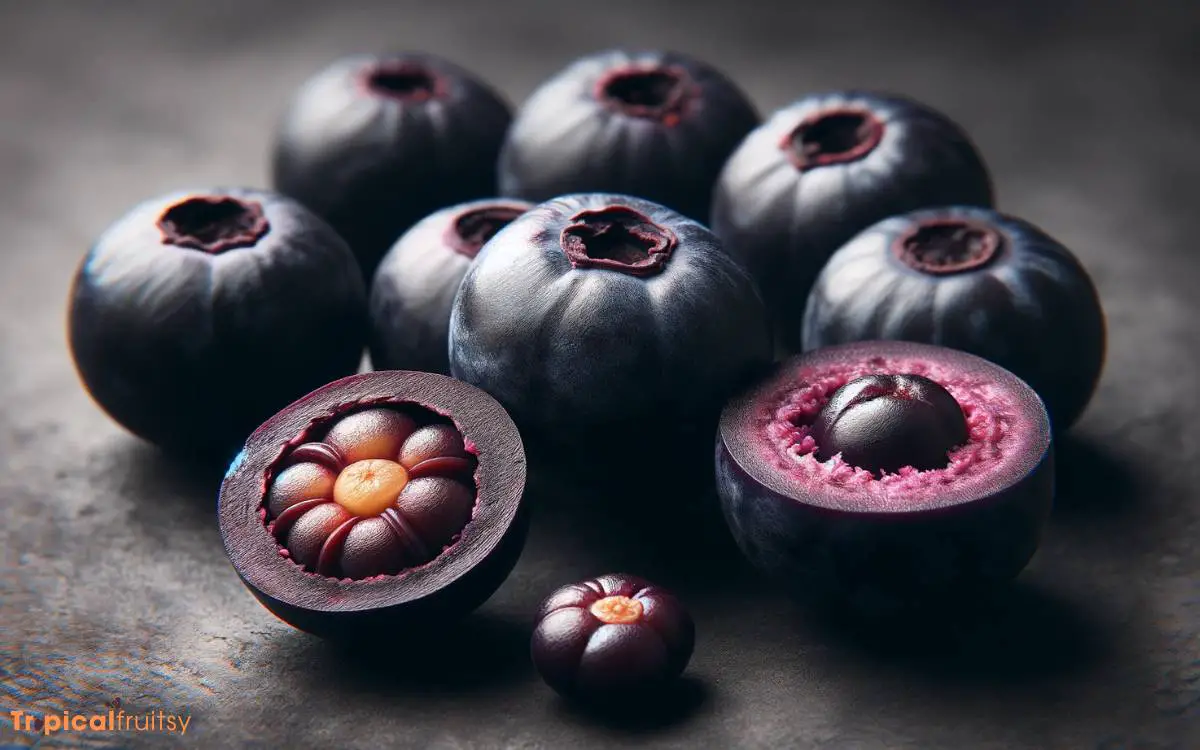

Acai berries are small, round, and dark purple in color. They grow on the acai palm tree, which is native to the rainforests of Central and South America.
The berries have a diameter of about 1-2 centimeters (0.4-0.8 inches) and are typically covered by a tough outer skin that surrounds a large seed.
The edible part of the berry is the pulp, which is dark purple and has a unique flavor that is often described as a combination of berries with a hint of chocolate.
Acai berries gained popularity due to their reported health benefits and high antioxidant content.
They are commonly consumed in smoothie bowls, juices, and various health food products.
Keep in mind that acai berries are perishable and are often processed into frozen puree or dried powder for export and commercial use.
Is Acai Berry Puree as Nutritious as Whole Acai Berries?
Acai berry puree explained: Acai berry puree contains the same nutrients as whole acai berries. However, the puree form allows for easier consumption and can be added to smoothies, yogurt, or oatmeal. Both forms offer the same health benefits, such as antioxidants and fiber, making them equally nutritious options.
Do Acai Berries Have Seeds
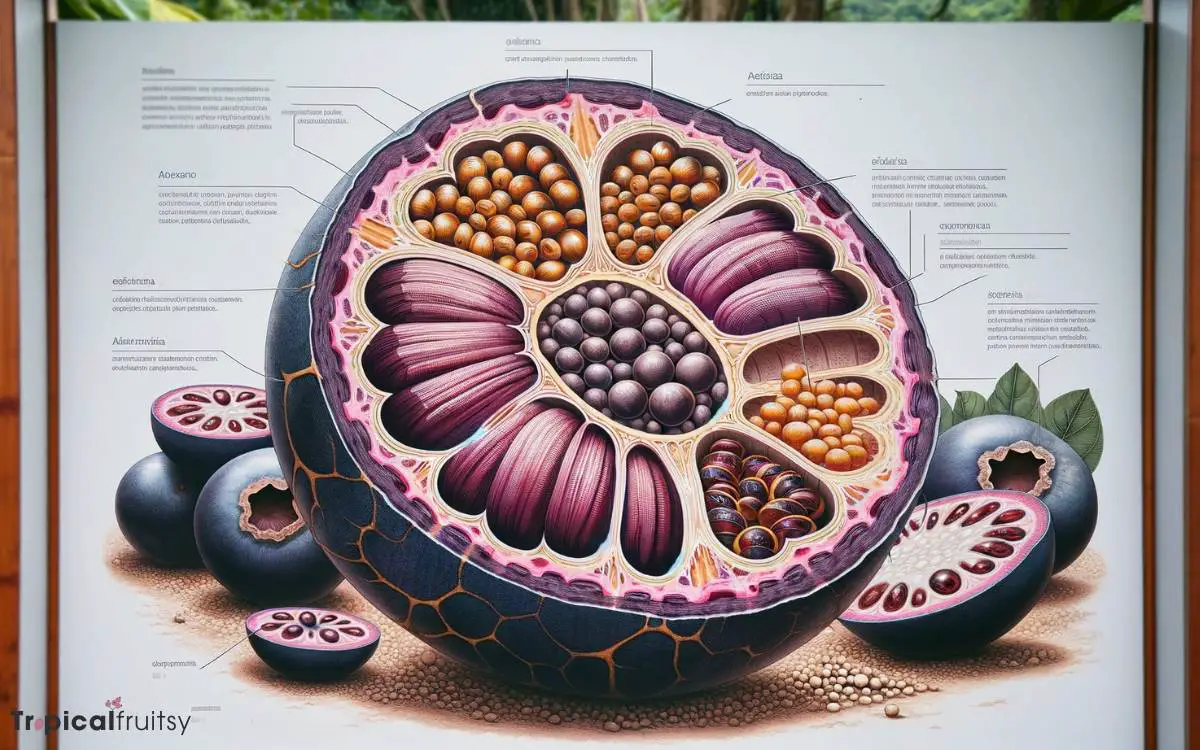

Yes, acai berries have a large seed at the center, which makes up a significant portion of the berry. The seed is usually covered by a thin layer of pulp.
When acai berries are processed for consumption, the seed is typically removed, and the remaining pulp is used to make acai products like frozen puree, acai bowls, juices, or supplements.
The pulp is the part of the berry that is rich in nutrients and gives acai its distinctive flavor and dark purple color.
Conclusion
The acai berry stands as a nutritional beacon, offering a myriad of health benefits akin to a treasure chest for those invested in their well-being.
With its deep roots in history and traditional medicine, and a profile enriched with antioxidants, it garners attention in the realm of superfoods.
As a sustainable harvest, it also contributes positively to the environment, making it not just a choice for personal health, but a nod to ecological mindfulness.






