Where Are Acai Berries from? Amazon Rainforest Roots!
Acai berries are native to the rainforests of Central and South America, thriving predominantly in the Amazon Basin.
This region’s climate and fertile floodplains create the perfect conditions for acai palm trees to grow and bear fruit.
The acai palm, known scientifically as Euterpe oleracea, is indigenous to tropical rainforests. The Amazon Basin, with its unique ecosystem, is the primary area where these trees are found.
Acai berries have been part of the indigenous diet for centuries and are now recognized globally for their potential health benefits.
Acai berries’ journey from the lush Amazon to worldwide acclaim underscores their status as a nutrient-packed superfood.

Key Takeaway
Açaí Palm Distribution and Significance
| Country | Habitat | Significance | Global Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Amazon Basin rainforests | Staple in indigenous diet | Superfood |
| Peru | Amazon Basin rainforests | Source of nutrition and health | Internationally recognized |
| Venezuela | Amazon Basin rainforests | Traditional food source | Exported globally |
Unveiling the Acai Origin
The acai berry’s origin lies in the rainforests of the Amazon basin, primarily within the territory of Brazil.
This small, dark purple fruit is harvested from the acai palm tree, known scientifically as Euterpe oleracea, which thrives in the region’s unique alluvial floodplains.
The berries have been a staple in the diet of indigenous communities for centuries, valued for their nutritional content and medicinal properties.
Scholarly research indicates that these berries are rich in antioxidants, which are believed to have numerous health benefits.
The precise ecological conditions of the Amazon, including its rich soil and humid climate, are critical to the growth of acai palms.
Understanding the interplay between the acai berry and its environment is essential for sustainable harvesting practices.
This segues into the importance of preserving the delicate Amazonian habitat where the acai berry proliferates.
The Amazonian Habitat

The Amazonian Habitat is a vast rainforest ecosystem spanning over 5.5 million square kilometers. It provides an intricate network of ecological relationships and environmental conditions essential for the growth of acai berries.
Renowned as a biodiversity hotspot, this region supports a multitude of flora and fauna. It is home to numerous endemic species that have adapted to the unique climatic and soil conditions of the forest.
The proliferation of the acai palm within this habitat underscores the interdependence between the species and its native environment. This dynamic is critical to the sustainability of the ecosystem.
Rainforest Ecosystem
Acai berries originate from the biodiverse rainforest ecosystems of the Amazon Basin, which is home to an estimated 390 billion individual trees and thousands of species of flora and fauna.
This complex habitat can be depicted through the following characteristics:
- Unparalleled Biodiversity: The Amazon Rainforest is one of the most species-rich areas on Earth, hosting myriad plant and animal species, many of which are endemic to the region.
- Dynamic Climatic Conditions: The ecosystem is shaped by a warm, humid climate facilitating a year-round growing season, which influences the life cycles and reproductive patterns of the residing species.
- Interconnectedness: Symbiotic relationships and intricate food webs are central to the ecological integrity, where species rely on one another for survival.
- Threats and Conservation: Human activities pose significant threats to the rainforest’s ecological balance. Efforts to preserve and restore this habitat are critical for maintaining its biodiversity, which includes the acai palm.
In this analytical context, the Amazonian rainforest is not merely a backdrop for the acai berry’s existence but a complex, living system that requires careful study and protection.
Biodiversity Hotspot
Originating in the Amazon Basin, acai berries thrive within one of the world’s most crucial biodiversity hotspots. This region supports an unparalleled variety of life, offering a complex network of ecosystems.
The Amazon’s biodiversity is not merely a collection of species but a web of intricate relationships and ecological processes.
The preservation of this habitat is vital for maintaining the genetic diversity necessary for species adaptation and survival.
| Amazonian Features | Importance | Threats |
|---|---|---|
| Diverse Ecosystems | Genetic Variability | Deforestation |
| Endemic Species | Ecological Stability | Climate Change |
| Rich Plant Life | Medicinal Resources | Illegal Exploitation |
Analyzing this tableau reveals the Amazon’s pivotal role in fostering a myriad of species, including endemic varieties that flourish in its unique environment.
To understand the full scope of the Amazon’s ecological significance, one must also consider the specific growth patterns of these endemic species.
Endemic Species Growth
Within the Amazonian habitat, endemic species like the acai berry exhibit growth patterns that are intricately adapted to the region’s unique climatic and soil conditions.
The survival and proliferation of Euterpe oleracea, the species known for its acai berries, can be attributed to a number of key factors:
- High Rainfall: The Amazon rainforest’s high precipitation levels provide the necessary moisture for acai palms to thrive.
- Rich Biodiversity: The surrounding biodiversity creates a complex ecosystem that supports various life forms, including pollinators crucial for acai berry production.
- Floodplain Ecosystems: Acai palms are often found in areas prone to seasonal flooding, which contributes to soil fertility and provides a natural irrigation system.
- Canopy Layering: The acai palm grows well in the understory layer of the forest, utilizing the filtered sunlight that penetrates the canopy.
This specialized adaptation ensures that acai berries are a product of a habitat uniquely suited to their growth.
History in Indigenous Cultures
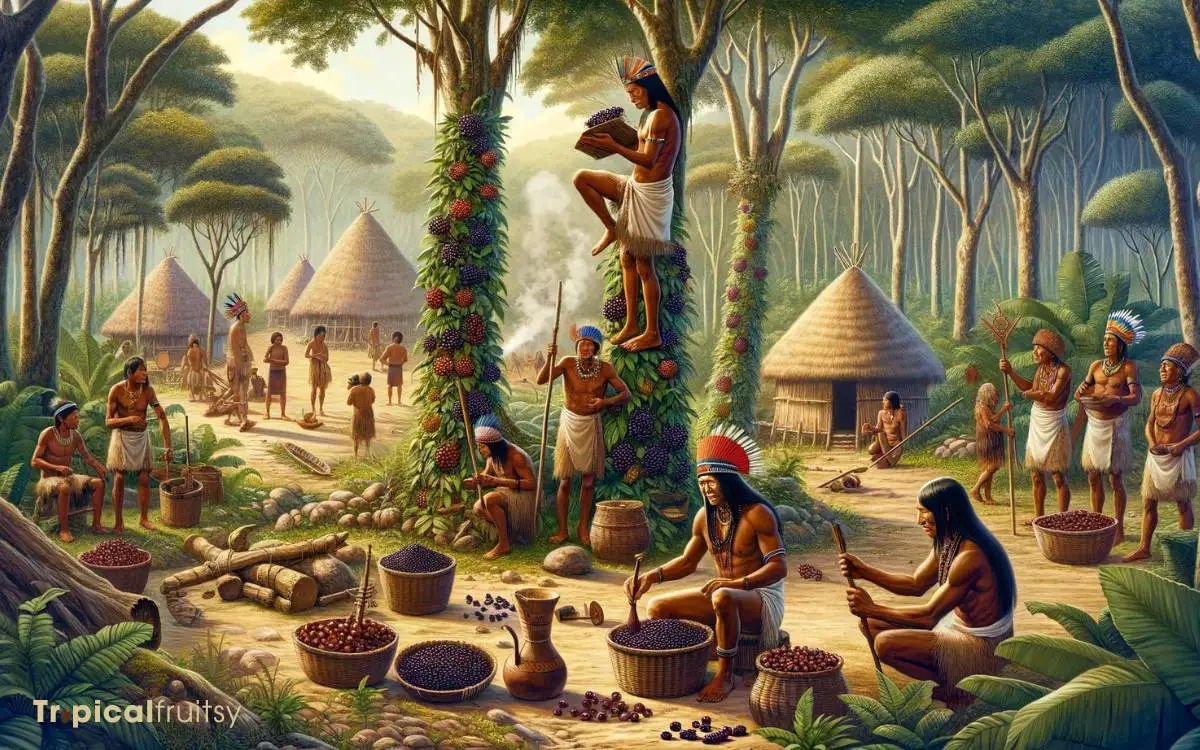

Acai berries, indigenous to the Amazon basin, have been integral to the diets and medicinal practices of the region’s tribes for centuries.
Their traditional uses extend beyond nutrition, as the fruit occupies a vital role in the cultural narratives and ceremonial practices of these communities.
An analysis of the acai berry’s historical application by indigenous cultures reveals its multifaceted importance, potentially offering insights into sustainable harvesting practices that honor both ecological and cultural heritage.
Traditional Uses
While acai berries are now known globally for their health benefits, historically, indigenous tribes of the Amazon rainforest have utilized them as a staple food source and for medicinal purposes.
The traditional applications of acai berries within these communities are diverse:
- Nutritional sustenance: Acai berries provided a rich source of calories and essential nutrients, supporting the daily dietary needs of the tribes.
- Medicinal concoctions: Tribespeople often used acai berries to treat various ailments, including digestive issues, skin conditions, and infections.
- Ritual practices: The berries played a role in certain spiritual ceremonies, where they were consumed for their perceived vitality-enhancing qualities.
- Trade commodity: Acai also served as a valuable item for bartering among different tribes and with early European colonizers.
This multifaceted role of acai berries laid the groundwork for their profound cultural significance, which will be explored in the following section.
Cultural Significance
The cultural heritage of indigenous Amazonian tribes is deeply intertwined with the use of acai berries, reflecting their historical importance beyond mere sustenance.
Acai berries have not only been a nutritional cornerstone but also a symbol of vitality and health within these communities.
The harvesting and preparation of acai are steeped in traditional practices that have been passed down through generations, embodying a wealth of ethnobotanical knowledge.
These customs articulate a relationship with the environment that is both respectful and symbiotic, with the acai palm playing a central role in local cosmology and social rituals.
In examining the cultural tapestry of Amazonian indigenous groups, the acai berry emerges as an emblematic fruit that encapsulates the intricate bond between people and their natural heritage.
Nutritional Profile Breakdown
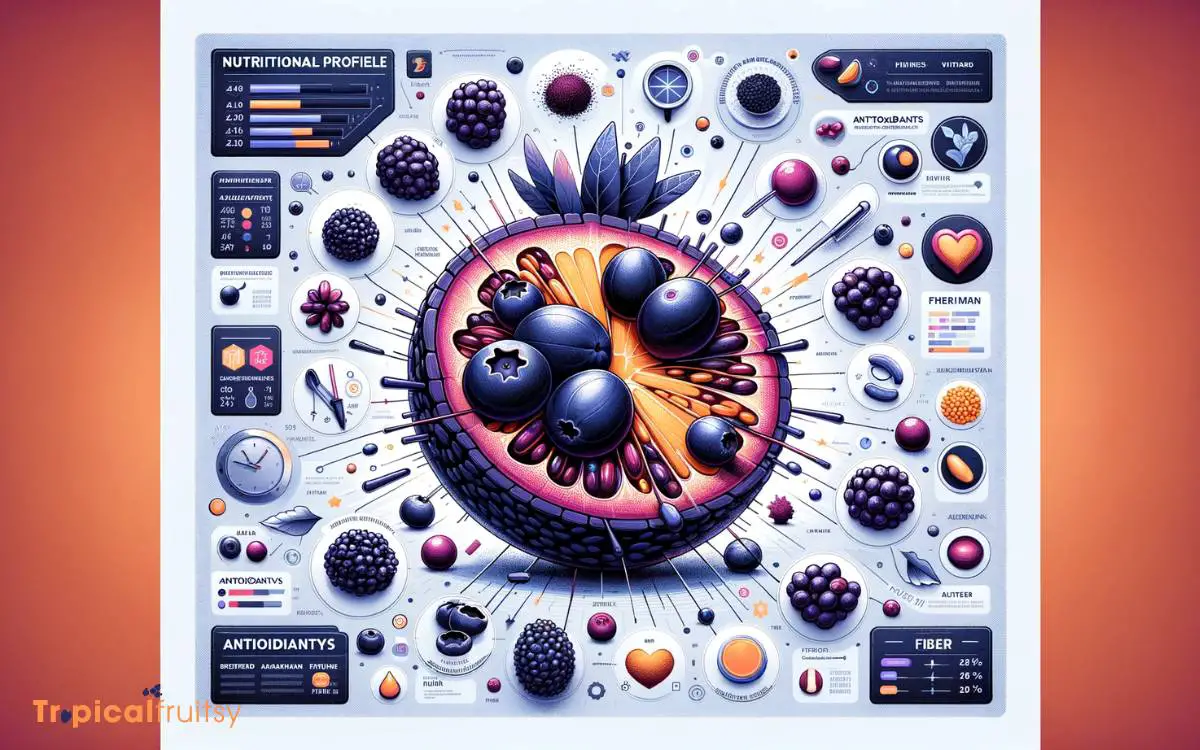

Originating from the Amazon rainforest, acai berries boast a nutrient-dense profile rich in antioxidants, fiber, and heart-healthy fats.
These dark purple fruits have garnered attention within nutritional science for their potential health benefits, which stem from their comprehensive array of vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals.
To elucidate the nutritional composition of acai berries, consider the following:
- Antioxidants: Acai berries are exceptionally high in anthocyanins, compounds known for their potent antioxidant properties.
- Fiber: A single 100-gram serving provides approximately 2 to 3 grams of dietary fiber, aiding in digestive health.
- Fats: The berries contain monounsaturated fats, such as oleic acid, contributing to cardiovascular health.
- Essential Amino Acids: Acai berries include an almost complete profile of essential amino acids, supporting protein synthesis.
This analysis reflects acai berries’ standing as a superfood, with implications for various aspects of health maintenance and disease prevention.
Harvesting Practices
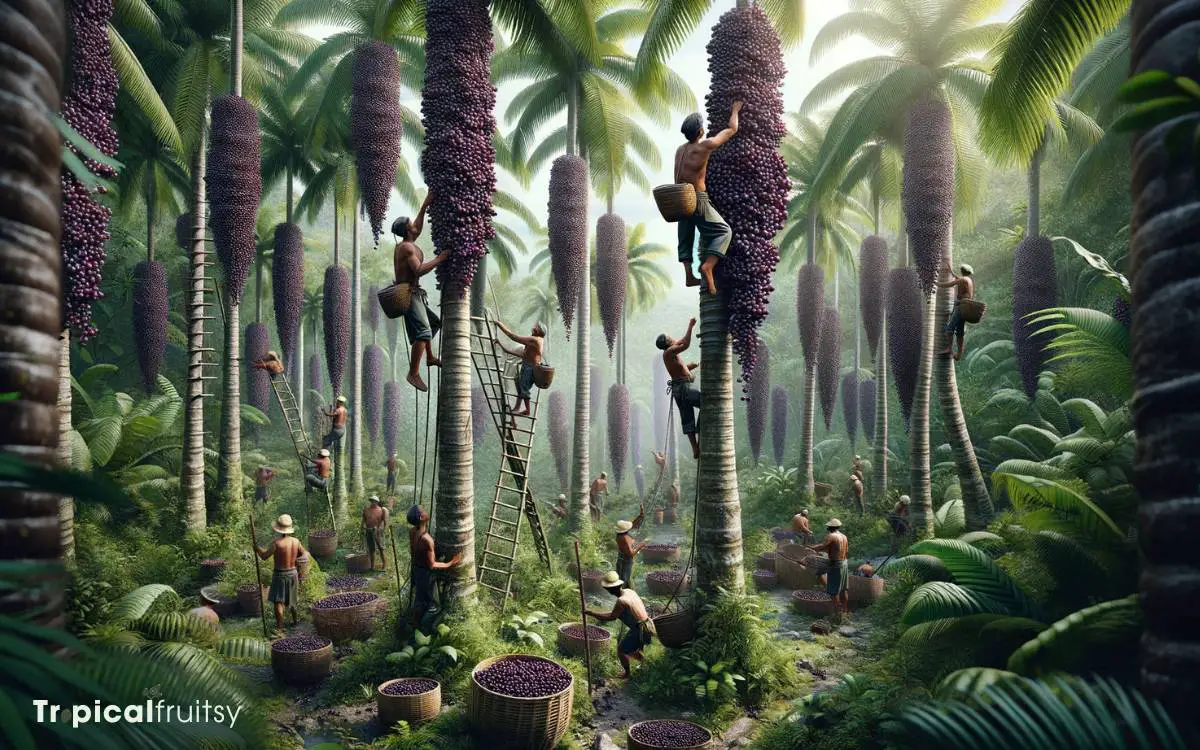

Acai berries are typically hand-picked by local farmers in the dense Amazonian forest, employing sustainable methods that protect the delicate ecosystem.
This labor-intensive process requires skill and precision, as the acai palm trees can grow to significant heights, necessitating the use of ladders or climbing techniques.
The harvesting practices are often closely aligned with traditional methods that have been passed down through generations, reflecting an intrinsic understanding of the forest’s rhythms and the importance of preserving its resources.
To ensure clarity and conciseness, the table below provides an overview of key elements in acai berry harvesting practices:
| Aspect | Detail | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Harvest Method | Hand-picked | Minimizes damage to trees and berries |
| Timing | Seasonal, aligned with natural ripening cycles | Ensures peak nutritional value |
| Preservation | Immediate freezing or drying post-harvest | Maintains freshness and nutrients |
| Local Economy | Provides income for indigenous communities | Supports sustainable livelihoods |
| Environmental Impact | Low; sustainable practices preserve biodiversity | Promotes forest conservation |
What Are the Origins of Acai Berries and Where Can They Be Found?
Acai berries are native to the Amazon rainforest in Brazil, where they have been a staple in the diet of indigenous tribes for centuries. These nutrient-dense berries are now popular worldwide for their numerous acai berry extract benefits and can be found in health food stores and specialty markets.
Global Journey to Superfood Fame

From their humble beginnings in the Amazon, acai berries have ascended to global prominence as a celebrated superfood.
This meteoric rise can be attributed to a confluence of factors that have been meticulously documented and analyzed by nutritionists and food marketers alike.
- Nutritional Research: Scientific studies highlighted the berry’s high antioxidant content, linking it to health benefits such as anti-aging and weight loss.
- Media Exposure: Influential health experts and celebrities endorsed acai products, propelling its popularity.
- Marketing Strategies: Marketers adeptly positioned acai as an exotic health food, leveraging its Amazonian origin for brand mystique.
- Globalization of Diets: An increased focus on health-conscious living worldwide created a fertile ground for acai products to flourish in various markets.
Each of these elements synergistically amplified the demand for acai, transforming it from a regional staple into an international dietary phenomenon.
Conclusion
The acai berry’s journey from the Amazon rainforest to international acclaim as a superfood encapsulates a complex narrative of cultural heritage, ecological significance, and nutritional discovery.
While some may argue that global demand has led to exploitation, sustainable harvesting practices have been implemented to balance economic growth with environmental stewardship.
Thus, the acai berry remains not only a source of healthful nutrients but also a symbol of the intricate interplay between nature and culture.