Why Is Durian Fruit Banned? Discover the Forbidden Delicacy!
The durian fruit is banned in various public spaces and on transportation due to its overpowering smell, which can be offensive to some people.
This tropical fruit’s scent has been likened to rotten onions or sewage, leading to its prohibition to ensure the comfort and welfare of the public in shared environments.
The bans also extend to certain international import regulations, reflecting the fruit’s contentious nature among consumers globally.
The reasons behind the banning of durian fruit include:
For example, in Singapore, durian is famously banned on the Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) system, with signs clearly indicating the prohibition.
Durian fruit’s ban underscores the delicate balance between cultural appreciation and public consideration.

Key Takeaway
Durian Ban Policies Across Different Locations and Contexts
| Location | Type of Ban | Reason for Ban | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Singapore MRT | Transportation | Strong odor affecting other passengers | Well-known ban, clearly indicated in stations |
| Various Hotels | Accommodation | Odor permeates rooms and common areas | Policies vary, with some hotels having designated durian areas |
| Airplanes | Transportation | Confined space intensifies smell | Some airlines forbid durian in carry-on or checked luggage |
| Import Controls | International Trade Regulation | Odor considered a public nuisance | Specific countries have strict controls over durian imports |
The Intense Aroma Explained
The pungent odor of durian fruit, often described as a unique combination of rotten onions, turpentine, and raw sewage, can be attributed to a complex blend of volatile sulfur compounds.
These chemical constituents, such as ethanethiol and methionine, are responsible for the fruit’s powerful and persistent smell, which can linger even after the fruit has been removed from an area.
Scientific analysis reveals that the odoriferous profile of durian is quite sophisticated, comprising at least 44 distinct odor-active compounds, each contributing to the overall sensory experience.
This aroma profile is highly distinctive, leading to polarized perceptions of the fruit’s appeal.
Understanding the biochemical makeup of durian’s scent is crucial to appreciating the reasons behind its controversial status in public spaces.
This leads us to consider the implications of durian’s potent fragrance on public transportation systems.
Public Transportation Restrictions
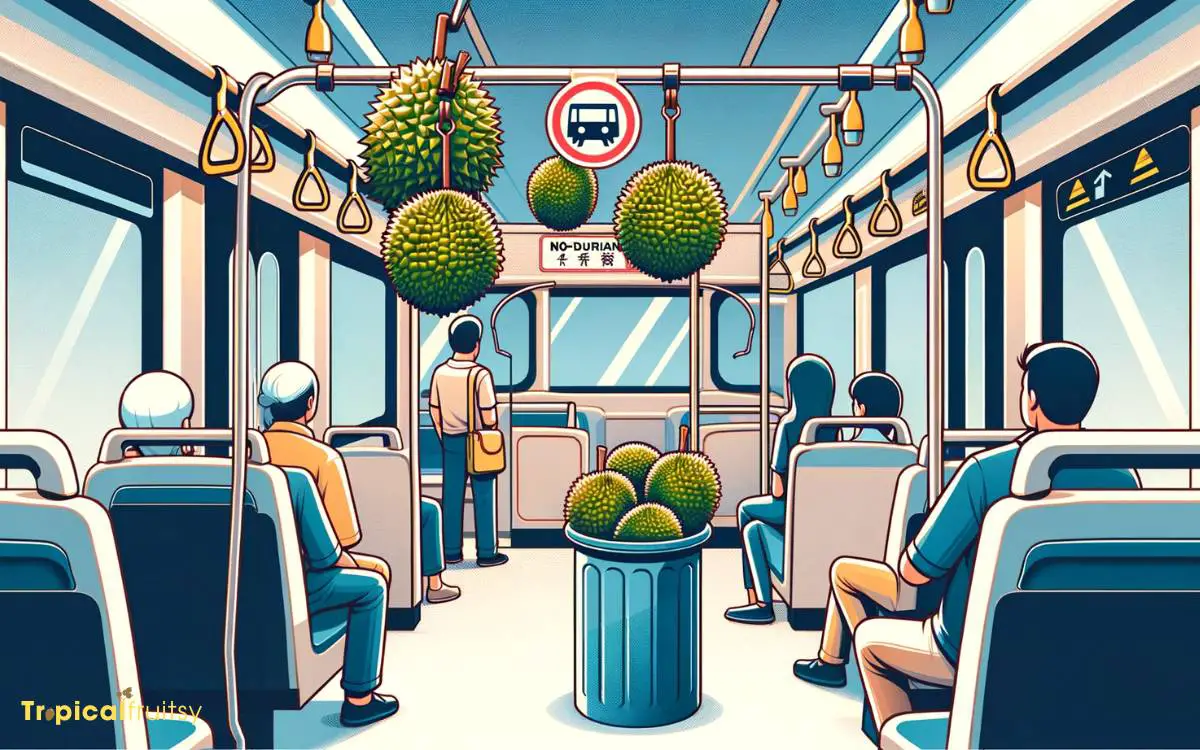

Public transportation systems globally have imposed restrictions on carrying durian fruit due to its potent odor, which can be pervasive and linger, affecting the enclosed environment and air quality within transit vehicles.
These measures prioritize passenger comfort and the maintenance of a pleasant communal travel space.
The prohibition is a response to complaints and operational concerns, ensuring that all passengers can enjoy a neutral-smelling atmosphere while commuting.
Odor Impact
Because the pungent aroma of durian fruit is perceived as overwhelmingly offensive to many individuals, numerous public transportation systems across Southeast Asia have implemented strict bans on the fruit to ensure passenger comfort.
This policy reflects a broader understanding of the social implications of durian consumption in shared spaces, as public transport providers strive to maintain a pleasant environment for all users.
- The intensity of durian odor can linger, affecting subsequent passengers even after the fruit is removed.
- Sensitivity to smells varies among individuals, making the fruit’s presence a potential source of discomfort.
- The enclosed nature of public transportation amplifies the perception of the odor.
- These restrictions aim to avoid conflicts between passengers caused by the divisive scent.
Policies are often enforced with fines or other penalties to underscore their importance and ensure compliance.
Passenger Comfort Concerns
How do public transportation bans on durian fruit reflect concerns for passenger comfort and the collective experience of travel?
The prohibition of durian on public transportation systems underscores a commitment to maintaining a pleasant and welcoming environment for all passengers.
The durian’s pungent odor is often perceived as overwhelming and can infiltrate enclosed spaces, making it a significant discomfort for some travelers.
These restrictions are evidence of the transit authorities’ efforts to balance individual freedoms with the public good, ensuring that the shared space remains accessible and enjoyable for everyone.
| Aspect | Impact | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Odor Intensity | High | Potent smell affects passengers’ comfort |
| Enclosed Spaces | Amplifies Odor | Limited airflow in public transport intensifies scent |
| Public Opinion | Mostly Negative | Majority of passengers prefer odor-free surroundings |
| Cultural Sensitivity | Varied | Acceptance of durian’s smell differs by region |
| Policy Management | Necessary | Rules ensure a balance between personal choice and communal well-being |
Health Concerns and Myths

Addressing health concerns, myths surrounding the durian fruit have contributed to its ban in various public spaces.
While durian is nutritious, providing high energy content and rich in vitamins, certain misconceptions have been perpetuated, affecting its acceptance.
An analytical examination of prevalent myths reveals:
- Durian’s high sulfur content is believed to induce digestive distress or exacerbate heartburn.
- Myths suggest that consuming durian with alcohol can lead to severe indigestion or even fatality.
- Some people claim that the fruit’s potent aroma can cause headaches or nausea in sensitive individuals.
- A persistent belief is that durian’s heaty nature can lead to an imbalance in body humors, despite a lack of scientific evidence.
These points underscore the need for an objective differentiation between fact and myth in discussions related to durian’s health implications.
Durian’s Cultural Significance

Why does durian, often revered as the ‘king of fruits’ in Southeast Asia, face bans in public spaces despite its cultural significance?
This thorny fruit embodies a dichotomy: a cultural icon and a source of polarizing controversy.
The durian is deeply integrated into the social and culinary fabric of the region, where it is celebrated in festivals and enjoyed in myriad culinary applications. Yet, its potent aroma has led to its prohibition in certain settings.
| Country | Cultural Significance | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
| Thailand | Integral to gastronomy | Banned in mass transit |
| Malaysia | Symbol of national pride | Prohibited in hotels |
| Singapore | Celebrated in festivals | Not allowed on public transport |
| Indonesia | Used in traditional ceremonies | Restricted in some public areas |
| Vietnam | Associated with hospitality | Limited in urban accommodations |
This complex relationship between cultural appreciation and public policy sets the stage for examining why establishments such as hotels and public spaces impose durian bans.
Hotels and Public Spaces Ban

The ban on durian fruit in hotels and public spaces primarily stems from its pungent odor, which can cause significant discomfort to individuals unaccustomed to the scent.
Establishments implement such policies to maintain a pleasant and neutral environment for all patrons, balancing the interests of durian enthusiasts with those of the general public.
The enforcement of these bans necessitates a nuanced approach to cultural sensitivity, as the fruit holds a beloved status in certain regions.
Odor Discomfort
Odor emanating from durian fruit is the primary reason for its prohibition in various hotels and public spaces.
This distinctive smell, often described as overpowering and persistent, can be a source of discomfort and complaint among patrons who are not accustomed to it.
The decision to ban durians is typically based on maintaining a pleasant and neutral environment for all customers.
The reasons for such bans are multifaceted:
- Intensity of Smell: The pungent aroma can permeate fabrics and linger in rooms long after the fruit has been removed.
- Customer Consideration: Ensuring the comfort of a broad clientele by preventing possible olfactory offense.
- Brand Image: Associations with unpleasant odors can adversely affect the reputation of an establishment.
- Health Concerns: In rare instances, the smell may trigger allergic reactions or asthmatic symptoms in sensitive individuals.
Policy Rationale

Several establishments implement bans on durian fruit to ensure the comfort and satisfaction of all patrons by eliminating the risk of its intrusive scent.
While durian enthusiasts may find the aroma appealing, the pungent smell can be extremely off-putting to others, often lingering in enclosed spaces and permeating fabrics and materials, creating a less than ideal environment for a diverse clientele.
The following table delineates the core reasons behind such policies:
| Factor | Explanation | Impact on Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Odor Intensity | Durian’s strong scent can overpower enclosed spaces | Justifies immediate bans in many establishments |
| Patron Comfort | Ensuring a pleasant experience for all guests | Central to maintaining a hospitable atmosphere |
| Business Image | Association with unpleasant odors affects reputation | Motivates proactive measures to avoid negative perceptions |
These considerations reflect a careful balance of interests aimed at maintaining a welcoming ambiance for guests and preserving the business’s reputation.
Cultural Sensitivity
In the context of cultural sensitivity, hotels and public spaces often prohibit durian fruit to respect the diverse preferences and olfactory sensitivities of their international clientele.
These establishments prioritize the comfort of their guests, recognizing that the strong aroma of durian—though cherished by some—can be overwhelmingly unpleasant to others.
The banning of durian fruit in such venues is therefore a measure of courtesy, reflecting a nuanced understanding of global cultural dynamics.
To add depth to this discussion:
- The pungent smell of durian is likened to rotten onions or raw sewage by those unaccustomed to it.
- Frequent travelers expect international standards of comfort and amenities.
- Negative olfactory experiences can deeply affect a guest’s perception of a place.
- The ban reflects a balance between local customs and global hospitality standards.
International Import Regulations

Although durian fruit is cherished for its taste in many parts of Southeast Asia, strict international import regulations are in place in various countries due to its pungent aroma and potential health concerns.
The intensity of its smell has led to outright bans in certain public spaces and modes of transport, influencing its acceptance on a global scale.
| Country | Regulation Detail |
|---|---|
| Singapore | Banned on public transport |
| Japan | Restrictions in public spaces |
| Australia | Strict quarantine checks required |
| United States | Import allowed, subject to inspection |
| European Union | Import permitted, health certificate needed |
Analyzing the table, it’s evident that regulations vary widely. Some countries focus on public comfort, others on biosecurity.
The restrictions underscore a balance between cultural appreciation and public health and safety standards.
The Love-Hate Relationship

Despite its popularity in Southeast Asia, durian fruit elicits strong reactions elsewhere due to its overpowering scent and distinctive taste, creating a divisive love-hate relationship among consumers worldwide.
The fruit’s unique characteristics have engendered an array of responses, with some celebrating its rich, custardy texture and others recoiling from its pungent aroma.
To further understand this polarizing perspective, consider the following points:
- Culinary Adventurism: Durian is often sought after by food enthusiasts eager to explore exotic flavors.
- Cultural Significance: In some cultures, durian is cherished as a delicacy and symbol of tradition.
- Sensory Response: The fruit’s intense smell can trigger extreme disgust or pleasure.
- Nutritional Value: Health-conscious individuals appreciate durian for its beneficial properties despite its contentious flavor profile.
An analytical approach reveals that the durian’s contentious status is as much about personal and cultural perception as it is about the fruit’s intrinsic qualities.
Durian Fruit Why Is It Illegal

Durian fruit is not universally illegal, but its importation, transportation, and consumption are restricted or banned in some places, primarily due to its pungent odor, which is often compared to rotten onions, raw sewage, or turpentine.
This strong smell is so pervasive that it can linger and spread through air conditioning systems, affecting large areas and making it quite unpleasant for those who find the odor offensive.
Here are a few specific contexts where durian has faced restrictions:
- Public Transportation: Many public transportation systems in countries where durian is popular, such as Singapore, Thailand, and Malaysia, have banned the fruit on buses, trains, and taxis to prevent the strong smell from discomforting other passengers.
- Hotels and Airplanes: Similarly, many hotels and airlines in Southeast Asia have prohibited durian because the odor can permeate through the air conditioning systems and linger in rooms and cabins, affecting other guests and passengers.
- Importation Bans: In some countries, there may be restrictions on importing durian due to agricultural regulations, but these are less about the smell and more about protecting local agriculture from pests and diseases that could be introduced with the fruit.
The bans and restrictions are more about managing the fruit’s strong odor in public spaces and during transport rather than an outright legal prohibition on the fruit itself.
Durian is widely available and consumed in countries where it is grown, with many people enjoying its unique taste despite the strong smell.
Conclusion
The durian fruit’s ban in various contexts is attributable primarily to its pungent aroma, which is potent enough to disrupt public environments and transportation systems. Additionally, misconceptions about health risks contribute to its exclusion.
Despite these challenges, durian remains culturally significant in many regions, illustrating a complex dynamic between cultural appreciation and public policy.
A notable instance is Singapore’s Mass Rapid Transit system, which enforces a strict prohibition to ensure passenger comfort.